Scam Sniffers charging policy has caused controversy. How should we choose the revenue from security tools?
When the addresses of bigwigs were attacked one after another and tens of millions of dollars were taken away by hackers, everyone found that the commonly used security tools began to generate income. Last week, the community discovered that Scam Sniffer, a security plug-in that is almost a must-have for cryptocurrency trading, suddenly had an inexplicable fee during transactions. It would insert instructions before signing to automatically deduct the fee. In the on-chain world where security is a top priority, this news aroused doubts from the community and users, and some users even directly uninstalled the Scam Sniffer plug-in.
On October 19, the official Scam Sniffer team said on the X account that they apologized for the inconvenience that the new fees for the Scam Sniffer plug-in product may cause to users, and Scam Sniffer is working hard to improve the notification function to increase transparency.
Scam Sniffer charges spark controversy
After checking the plugin interface and official website, BlockBeats reporters found that Scam Sniffer has set up a fee notification banner and updated the document to introduce the fee deduction details. In addition, the free version of the plugin has advanced features enabled by default, which has also aroused user doubts.
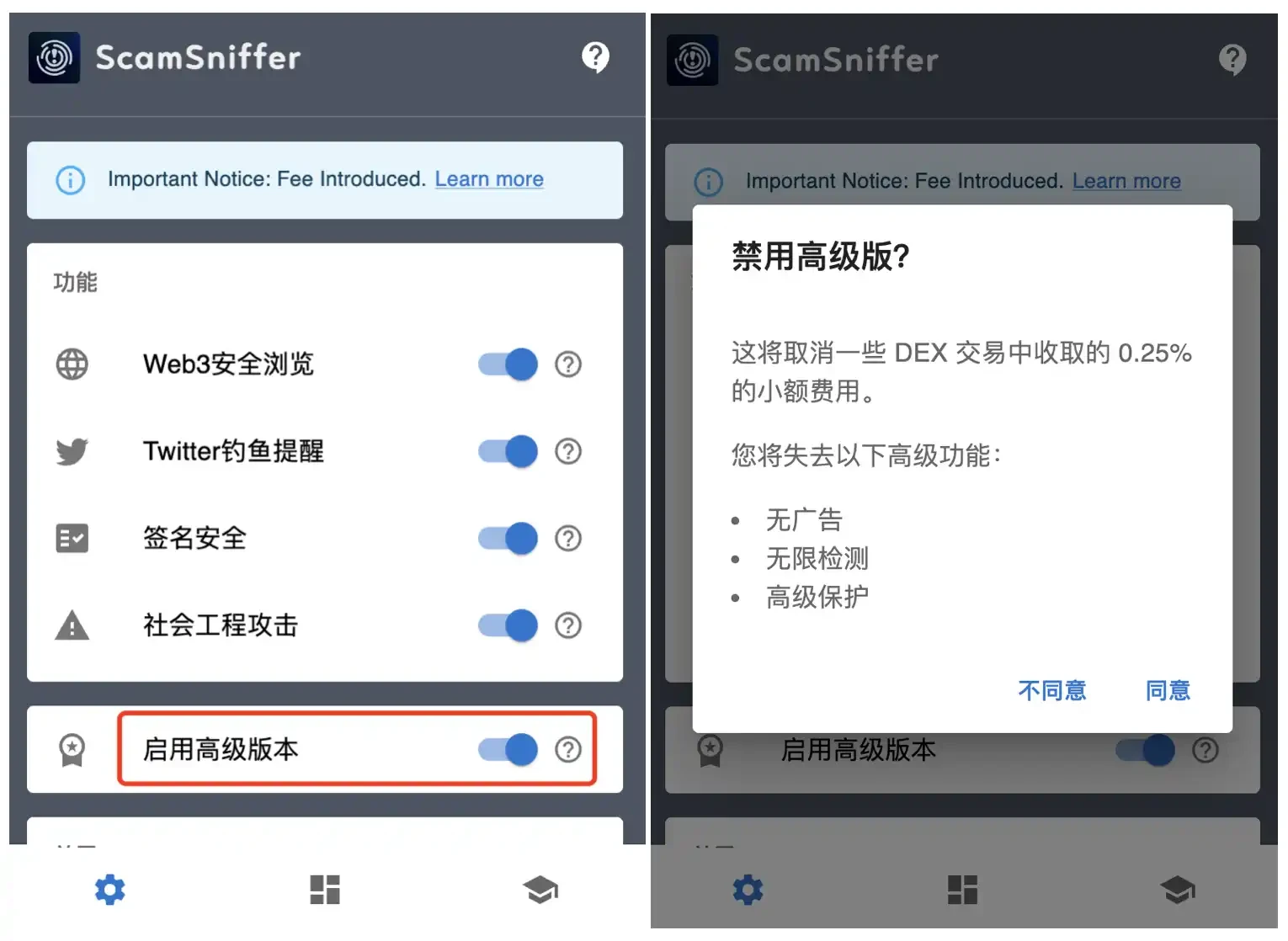
The official Scam Sniffer documentation shows that the plug-in implements the charging function by seamlessly integrating a custom instruction in the Uniswap universal router transaction. For specific DEXs, such as Uniswap and Pancake transactions, a fee of 0.25% will be charged. If the user disables the Enable Premium Plan option, some features will be unavailable, including ad removal, fewer detections, and a higher level of security protection.
In order to ensure users ability to pay and fairness, Scam Sniffer has set a monthly fee cap of $400 per address. In addition, the addresses of users who have purchased the plug-in will be whitelisted and will be exempt from any fees for the first three months, which means that Scam Sniffer has abandoned the buyout service and instead charged fees from each transaction, and said that future fees will become a default component of the product.
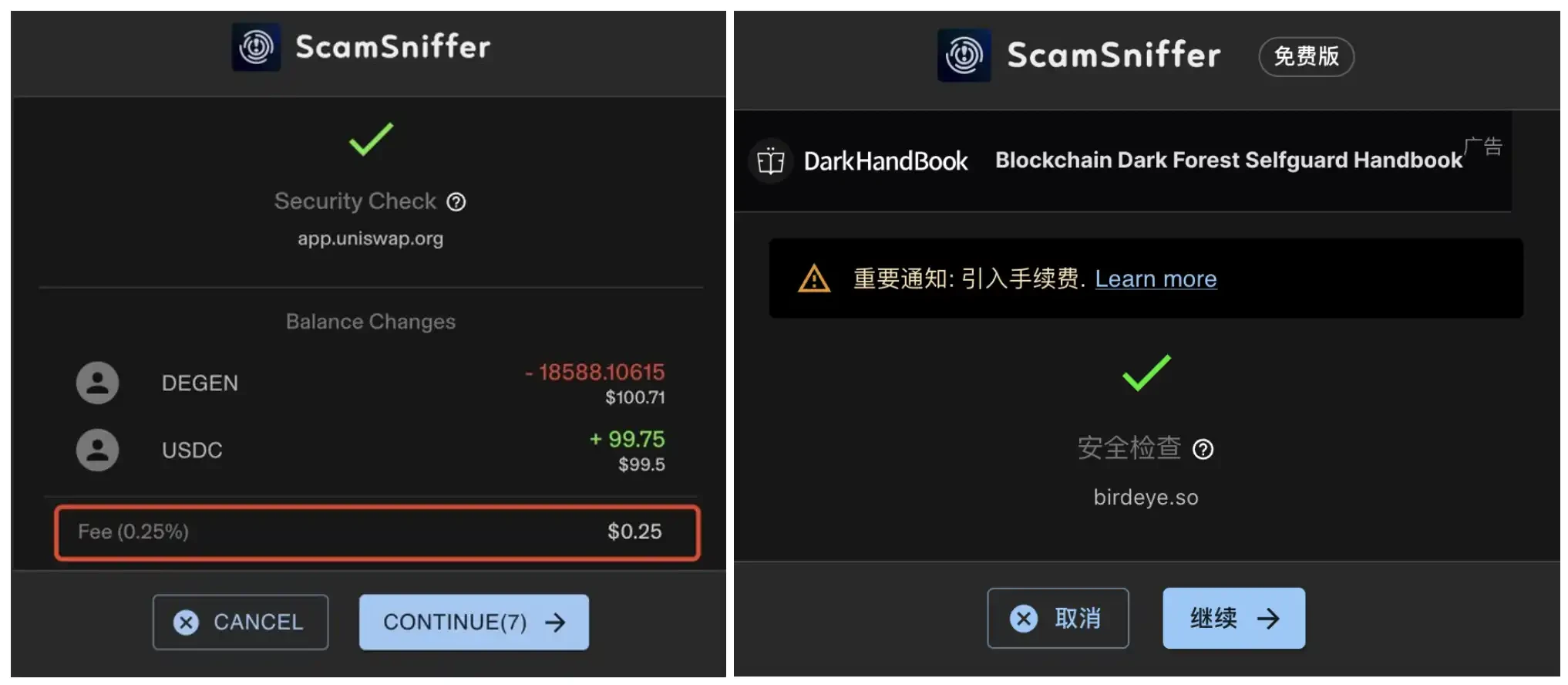
Left: The interface of the Scam Sniffer plug-in shared by a user before confirming a transaction; Right: The interface of the free version of the Scam Sniffer plug-in after adding a fee reminder and adding advertisements
In response to the charging controversy, Scam Sniffer emphasized that a transparent structure is crucial to winning user trust, and clear notifications can reduce confusion and improve user experience. It can be seen that Scam Sniffers charging plan has long been part of its product development strategy, and this response is more about the public opinion issue of failing to notify users in a timely manner.
Regarding users concerns about whether Scam Sniffer will tamper with transactions, BlockBeats confirmed with Mike, the founder of security company GoPlus, that the 0.25% fee charged by the Scam Sniffer plug-in for specific DEX transactions is the same as the fee charged by the Uniswap front-end and will not tamper with user transactions.
However, the community still has obvious differences on Scam Sniffers sudden payment plan. Some users think that it would be better to change the charging model to a recharge method, and to deduct subscription fees based on the number of detections or dates, saying that Scam Sniffer is a security plug-in that makes users worry about security. Another user pointed out the monopoly problem behind the charging, believing that such an exaggerated rate can only be charged because of the monopoly position.
However, some users are not sensitive to the charges themselves, but are more concerned about the product improvement and long-term benefits that the charges can bring. 0x AA, founder of WTF Academy, expressed support for Scam Sniffer charging, Compared to the losses from phishing, this fee is just a drop in the bucket, but the charges need to be transparent, otherwise users will lose trust. Another community user @BTW 0205 also believes that paying for use is not a big problem. If you can use the paid funds to develop better products, help more people avoid losses, and ensure the integrity of the teams operations, it is worth it.
It鈥檚 hard to make a living, what鈥檚 the correct way to make money?
This incident has also sparked discussion about the business model of the encryption security industry.
How to generate cash flow? This is the truth of making money that most founders and investors have been thinking about since this cycle. Since the exit logic of issuing coins-listing on the exchange-lying flat is no longer valid, it is better to learn the dividend philosophy that is popular in the current traditional market. After products such as Pump.fun and GMGN made huge profits in the meme market, this new logic of making money and exit seems to have been further proven.
When issuing coins is no longer the only business model, the projects ability to generate revenue becomes particularly important. Many products that already have PMF have also begun to figure out their own monetization paths, and the field of crypto security is one of them.
Are value-added services the answer?
Similar to traditional Internet security, blockchain security services are roughly divided into B-side and C-side. To B-side, the security of a blockchain project is divided into pre-chain and post-chain. Before chaining, it is mainly the security audit of smart contract code, and after chaining, there are real-time monitoring such as attack tracing and danger intelligence. On the C-side, it mainly involves services such as user wallet security and asset recovery.
For project owners, setting a security budget is a necessary expense, so it is relatively easier for security companies to promote their business on the B side. For ordinary users, although blockchain security is more urgent and necessary than traditional Internet, having a strong need does not mean that the business model of security services can easily achieve profitability.
Only when rigid demand is triggered in a specific scenario will the users willingness to pay become strong. For example, before the user accepts the fact that his assets have been stolen, transmitting the demand to the security company may prompt the user to pay. However, such scenarios are relatively low-frequency and difficult to expand, which means that it is difficult for companies that provide security services to C-end users to obtain stable cash flow. This may also be one of the considerations for Scam Sniffer to start a charging plan.
Yu Xian, the founder of SlowMist, mentioned in an interview with BlockBeats that users may be willing to pay high fees to recover stolen assets after the fact, but it is still a challenge to make users understand the value of security services and pay for them in advance. Mike, the founder of GoPlus, also emphasized this point. How to make users choose to pay actively before a security incident occurs through reasonable charges and value-added services is the key to determining the development of security products.
Scam Sniffer is not the first security product to adopt front-end charging. Pocket Universe, a security plug-in product launched in 2022, also charges a fixed fee for transactions on specific DEXs, with a fee rate as high as 0.8%. Kerberus Sentine l3, which acquired the security plug-in product Fire this year, also set a fixed fee of 8%.
However, the difference between these two products and Scam Sniffer is that they both offer insurance value-added services, that is, if the plug-in has scanned and did not warn the user of transaction risks, the user can seek compensation for lost assets. The compensation limit for Pocket Universe is $20,000, and the compensation limit for Sentine l3 is $30,000.
As for Sentine l3, not all users are eligible for claims. Sentine l3s product services are divided into free and paid versions. The paid version requires a fixed fee of 0.8%, and its functions include claim eligibility, RPC service, and anti-address pollution.
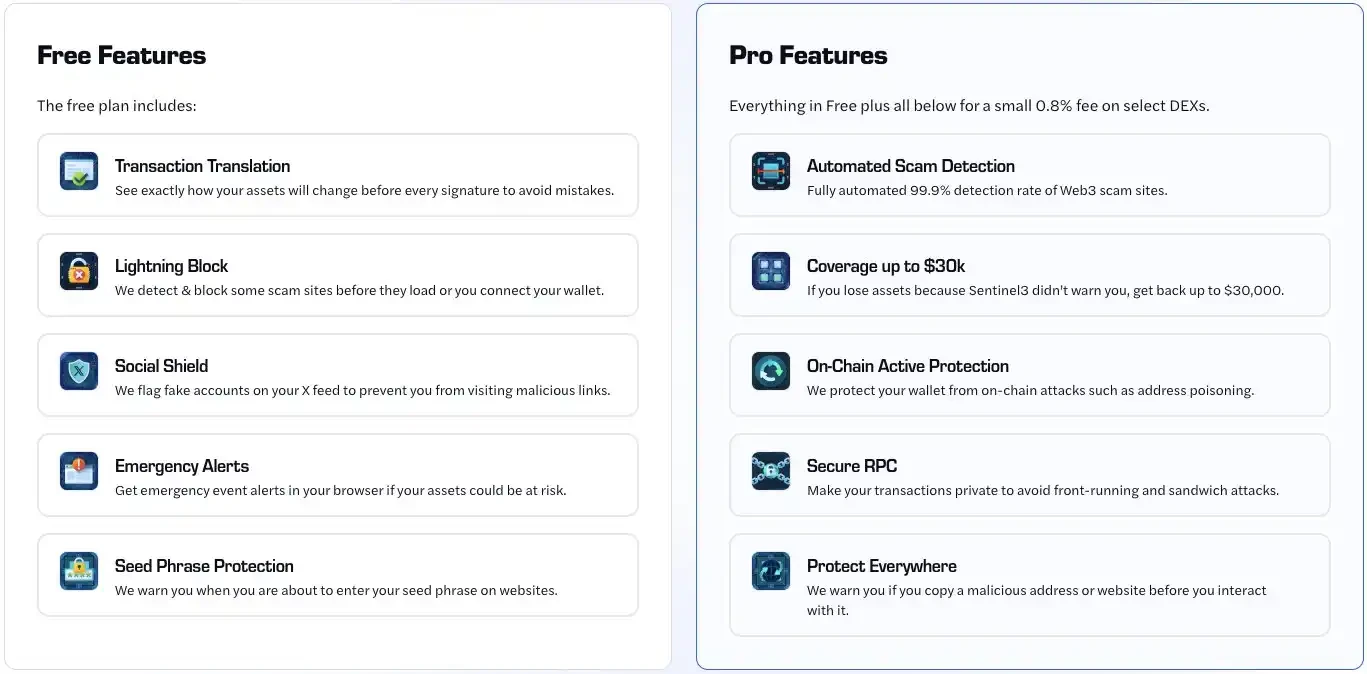
This business model of free and paid versions may be clearer and easier for users to accept than Scam Sniffers direct charging plan. Because some users, although they believe that security is important, are less receptive to charging for security services separately, especially when switching from free to paid.
However, even with clear product design and value-added services, actual market acceptance remains a challenge. For example, Stelo, a Web3 security company that received $6 million in funding from a16z, shut down all its products at the end of October last year because the team misjudged the market size, competition, and market maturity, resulting in its products not meeting expectations.
Stelo initially believed that as the number of users increased, the system would be able to continuously improve its ability to detect malicious transactions through network effects, eventually forming a positive cycle. However, reality has proven that most malicious transactions can be detected through simple rules and do not need to rely on network effects. In a market with no entry barriers, many competitors, and no strong network effects, Stelo failed to find a suitable profit model and eventually had to exit the market.
Security layer that retreats to the background
So how to achieve a sustainable profit model through innovative charging strategies and value-added services while ensuring user trust is a question that the current encryption security industry needs to think about.
But one trend that we have to realize is that if Web3 is compared to the Internet, we may have just entered the Windows XP/IE 6 browser era. Yu Xian believes that as the industry infrastructure gradually matures, many security products will retreat behind the scenes and become the default configuration, industry standards, and even user habits.
In this way, how blockchain security can be more deeply embedded in the underlying infrastructure in the future, making security a default service rather than an independent product module, further standardizing and intelligentizing it, improving the security level of the overall ecosystem, and thus reducing dependence on independent security plug-ins, will be a major trend in the development of the industry.
Mike, the founder of GoPlus, said that the future security infrastructure will be deployed at the grassroots level to solve all related problems for users. Whether it is DEX or wallet, they only need to call this security service layer to meet their security needs. This horizontal expansion means that security services will cover all major scenarios of users and form a unified security baseline.
At present, the security services on the C-end are still fragmented, and users need to integrate different security tools. This fragmentation leads to inconsistent user experience between different services and high integration costs. In the future, security services will be horizontally expanded and unified into an integrated solution. Enterprises only need to refer to this layer of security services to handle all security issues, so as to focus on their core business without having to solve the security needs of users separately.
Back to the business, according to a research report by Marketsand Markets, the blockchain security market size will grow from US$3 billion in 2024 to US$37.4 billion in 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 65.5%. This means that the encryption security industry still has a lot of room for development, but it also means that market competition will become increasingly fierce. Only those companies that can effectively integrate security technology, user needs and business models can stand out in this competition.
This article is sourced from the internet: Scam Sniffers charging policy has caused controversy. How should we choose the revenue from security tools?
Related: MATR1X FIRE Genesis Fire Test: Important Concepts FAQs
Matr1x Fire will have its first non-delete gold mining test in September 2024 – the Genesis Fire test. In this test, only the Genesis character NFT holders can participate in gold mining. We are looking for top Web3 game guilds around the world to cooperate. If you are interested, please click to fill in the information . This article will explain in detail the important concepts in this gold farming test and answer common questions. Important concepts and glossary You can click on this table to view the original text version. QA Tip: The numerical parameters in all the figures in this article are for illustrative purposes only and do not represent official test data. They are for reference only. 1. What is the Battle Pass and how do I…






