Delphi Digital: In-depth analysis of the opportunities and challenges of DeAI
Original author: PonderingDurian, Delphi Digital Researcher
Original translation: Pzai, Foresight News
Given that cryptocurrencies are essentially open source software with built-in economic incentives, and that AI is disrupting the way software is written, AI will have a huge impact on the entire blockchain space.
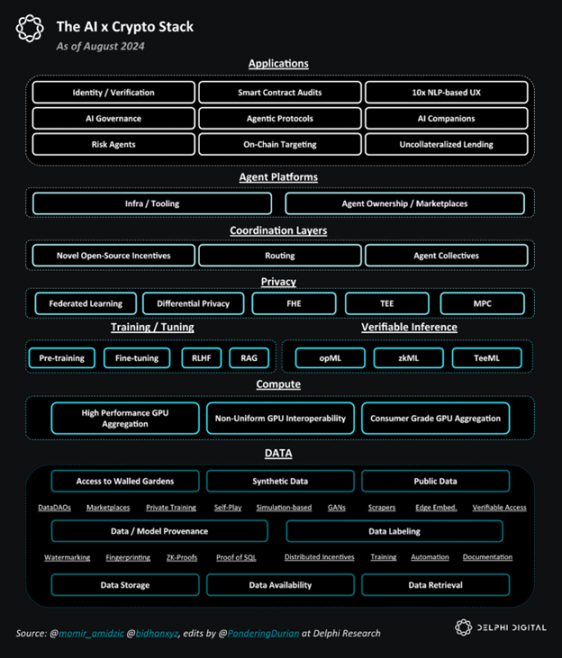
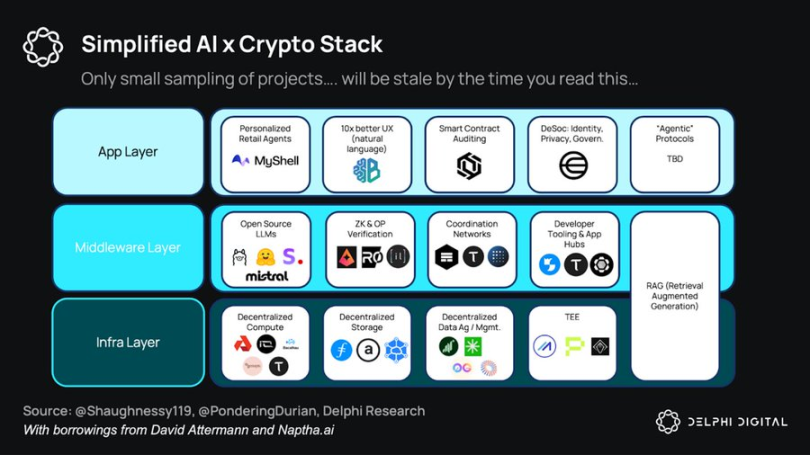
AI x Crypto Overall Stack
DeAI: Opportunities and Challenges
In my opinion, the biggest challenge facing DeAI lies in the infrastructure layer, because building basic models requires a lot of capital, and the returns to scale for data and computing are also high.
Given the law of scaling, tech giants have a natural advantage: having made huge profits from the monopoly profits of aggregating consumer demand during the Web2 phase and reinvested those profits in cloud infrastructure during a decade of artificially low rates, internet giants are now trying to capture the AI market by dominating data and computing (key elements of AI):
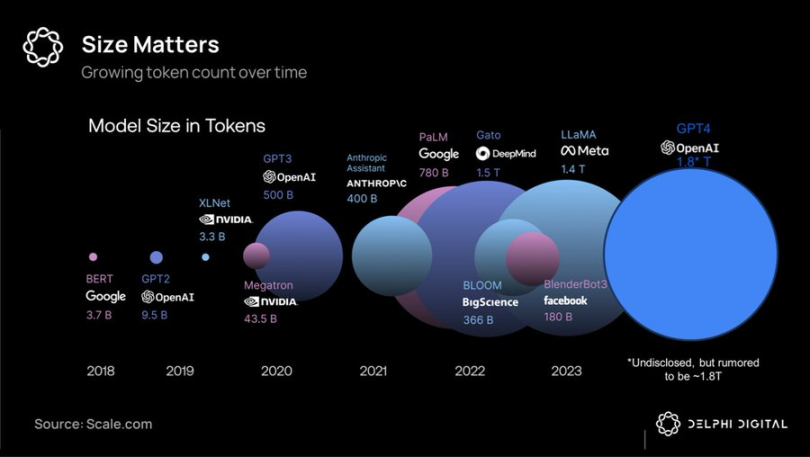
Token volume comparison of large model
Due to the capital intensity and high bandwidth requirements of large-scale training, unified superclusters remain the best option – providing the tech giants with the best performing closed-source models – which they plan to rent out at monopoly-like profits and reinvest the proceeds in each subsequent generation of products.
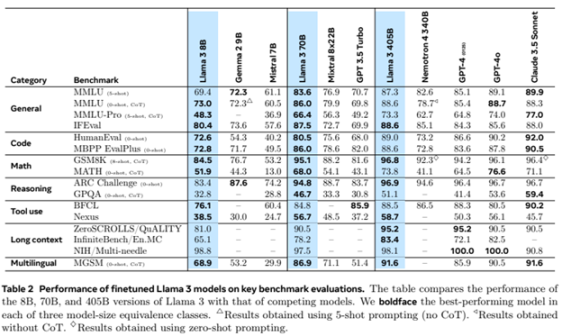
However, it turns out that the moat in the AI field is shallower than the Web2 network effect, and leading cutting-edge models are rapidly depreciating relative to the field, especially as Meta has adopted a scorched earth policy and invested tens of billions of dollars to develop open source cutting-edge models such as Llama 3.1, whose performance has reached SOTA levels.
Llama 3 Large Model Rating
At this point, combined with emerging research on low-latency decentralized training methods, it could commoditize (parts of) cutting-edge business models — as smartphone prices fall, competition would (at least partially) shift from hardware superclusters (which favors tech giants) to software innovation (which slightly favors open source/cryptocurrency).
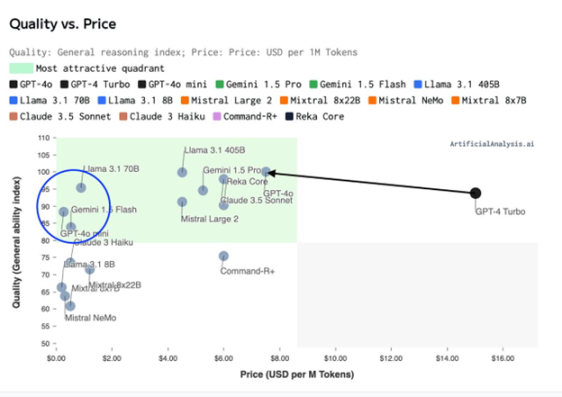
Capability Index (Quality) – Training Price Distribution Chart
Given the computational efficiency of “mixture of experts” architectures and large model synthesis/routing, we are likely facing not a world of 3-5 giant models, but a world of millions of models with different cost/performance tradeoffs. A network (hive) of interwoven intelligence.
This poses a huge coordination problem: one that blockchain and cryptocurrency incentive mechanisms should be able to help solve very well.
Core DeAI investment areas
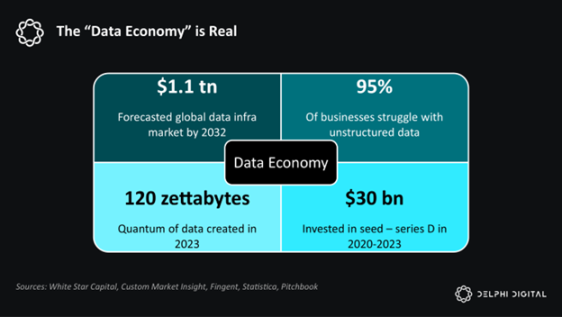
Software is eating the world. AI is eating software. And AI is basically data and compute.
Delphi is optimistic about the components in this stack:
Simplifying the AI x Crypto Stack
Infrastructure
Given that AI is powered by data and compute, DeAI infrastructure is focused on procuring data and compute as efficiently as possible, often using cryptocurrency incentives. As we mentioned earlier, this is the most challenging part of the competition, but given the size of the end market, it may also be the most rewarding part.
calculate
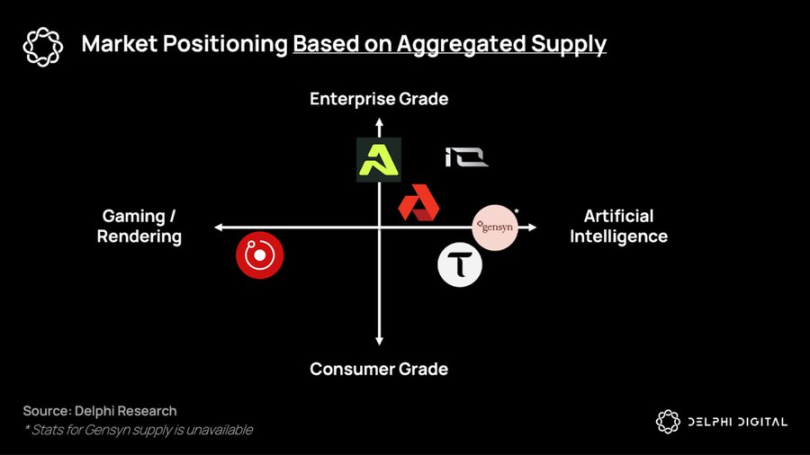
Distributed training protocols and the GPU market have been constrained by delays so far, but they hope to coordinate the potential of heterogeneous hardware to provide lower-cost, on-demand computing services to those who are locked out of the integrated solutions of the giants. Companies such as Gensyn, Prime Intellect and Neuromesh are driving the development of distributed training, while companies such as io.net, Akash, Aethir and others are enabling low-cost inference closer to edge intelligence.
Project niche distribution based on aggregated supply
data
In a world of ubiquitous intelligence based on smaller, more specialized models, data assets are increasingly valuable and monetizable.
To date, DePIN has been largely praised for its ability to build hardware networks at a lower cost than capital-intensive enterprises such as telecommunications companies. However, the largest potential market for DePIN will be in the collection of new types of data sets that will flow into on-chain intelligent systems: proxy protocols (discussed later).
In a world where the world’s largest potential market – labor – is being replaced by data and compute, De AI infrastructure provides a way for non-technical people to seize the means of production and contribute to the coming network economy.
middleware
The ultimate goal of DeAI is to enable efficient composable computing. Like the capital Lego of DeFi, DeAI makes up for the lack of absolute performance today through permissionless composability, incentivizing an open ecosystem of software and computing primitives to continue to compound over time, thereby (hopefully) surpassing existing software and computing primitives.
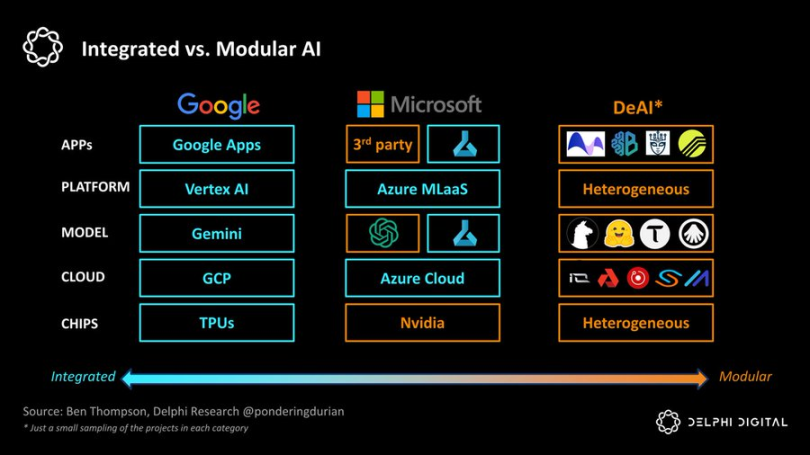
If Google is the extreme of “integration,” DeAI represents the extreme of “modularization.” As Clayton Christensen reminds us, in emerging industries, integrated approaches tend to lead by reducing friction in the value chain, but as the field matures, modular value chains gain ground by increasing competition and cost efficiency in each layer of the stack:
Integrated vs. Modular AI
We are very bullish on several categories that are critical to achieving this modular vision:
routing
In a world of fragmented intelligence, how can we choose the right mode and time at the best price? Demand-side aggregators have always captured value (see Aggregation Theory), and routing functions are critical to optimizing the Pareto curve between performance and cost in a world of networked intelligence: 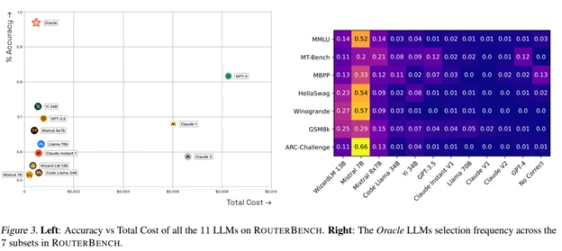
Bittensor has been at the forefront of the first generation of products, but a number of dedicated competitors have emerged.
Allora hosts competitions between different models in different “topics” in a “context-aware” and self-improving way over time, informing future predictions based on their historical accuracy under specific conditions.
Morpheus aims to be the “demand-side routing” for Web3 use cases — essentially an “Apple Intelligence” with an open-source local proxy that understands the relevant context of the user and can efficiently route queries through emerging building blocks of DeFi or Web3’s “composable compute” infrastructure.
Agent interoperability protocols such as Theoriq and Autonolas aim to push modular routing to the extreme, enabling a composable, composite ecosystem of flexible agents or components to become a fully mature on-chain service.
In summary, in a world where intelligence is rapidly fragmenting, supply-side and demand-side aggregators will be extremely powerful. If Google is a $2 million company that indexes the world’s information, then the winner of the demand-side router — whether it’s Apple, Google, or a Web3 solution — the company that indexes proxy intelligence will have much greater scale.
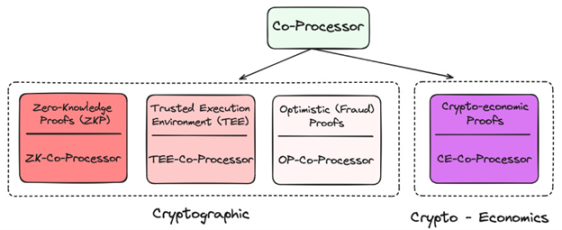
Coprocessor
Given its decentralized nature, blockchain is very limited in both data and computation. How do you bring the computationally and data-intensive AI applications that users need to blockchain? Through coprocessors!
Coprocessor application layer in Crypto
They all provide different techniques to verify that the underlying data or model being used is a valid oracle, which minimizes new trust assumptions on the chain while greatly improving its capabilities. To date, many projects have used zkML, opML, TeeML, and crypto-economic methods, and their advantages and disadvantages vary:
Coprocessor comparison
At a higher level, coprocessors are critical to the intelligence of smart contracts – providing a “data warehouse”-like solution to query for a more personalized on-chain experience, or to verify that a given inference was completed correctly.
TEE (Trusted Execution) networks such as Super, Phala and Marlin have become increasingly popular recently due to their practicality and ability to host large-scale applications.
Overall, coprocessors are critical to merging high-deterministic but low-performance blockchains with high-performance but probabilistic agents. Without coprocessors, AI would not be present in this generation of blockchains.
Developer Incentives
One of the biggest problems with open source development in AI is the lack of incentives to make it sustainable. AI development is highly capital intensive, and the opportunity costs of both computation and AI knowledge work are very high. Without the right incentives to reward open source contributions, the field will inevitably lose out to the supercomputers of hyper-capitalism.
From Sentiment to Pluralis, Sahara AI, and Mira, the goal of these projects is to launch networks that enable decentralized networks of individuals to contribute to the networks intelligence while giving them appropriate incentives.
By making up for it in the business model, the compounding rate of open source should accelerate – providing developers and AI researchers with a global alternative to big tech companies and the prospect of being well compensated based on the value they create.
While it is very difficult to do this and competition is increasingly fierce, the potential market here is huge.
GNN Model
While large language models classify patterns in large text corpora and learn to predict the next word, graph neural networks (GNNs) process, analyze, and learn from graph-structured data. Since on-chain data mainly consists of complex interactions between users and smart contracts, in other words, a graph, GNNs seem to be a reasonable choice to support on-chain AI use cases.
Projects such as Pond and RPS are trying to build basic models for web3, which may be applied in transactions, DeFi and even social use cases, such as:
-
Price prediction: On-chain behavioral models predict prices, automated trading strategies, sentiment analysis
-
AI Finance: Integration with existing DeFi applications, advanced yield strategies and liquidity utilization, better risk management/governance
-
On-chain marketing: more targeted airdrops/positioning, recommendation engine based on on-chain behavior
These models will make heavy use of data warehousing solutions such as Space and Time, Subsquid, Covalent and Hyperline, which I am also very bullish on.
GNN can prove that the big model of blockchain and Web3 data warehouse are essential auxiliary tools, that is, providing OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) functions for Web3.
application
In my opinion, on-chain agents may be the key to solving the user experience problem that crypto is well-known for, but more importantly, we have invested billions of dollars in Web3 infrastructure over the past decade, but the utilization on the demand side is pitiful.
Dont worry, here come the Agents…
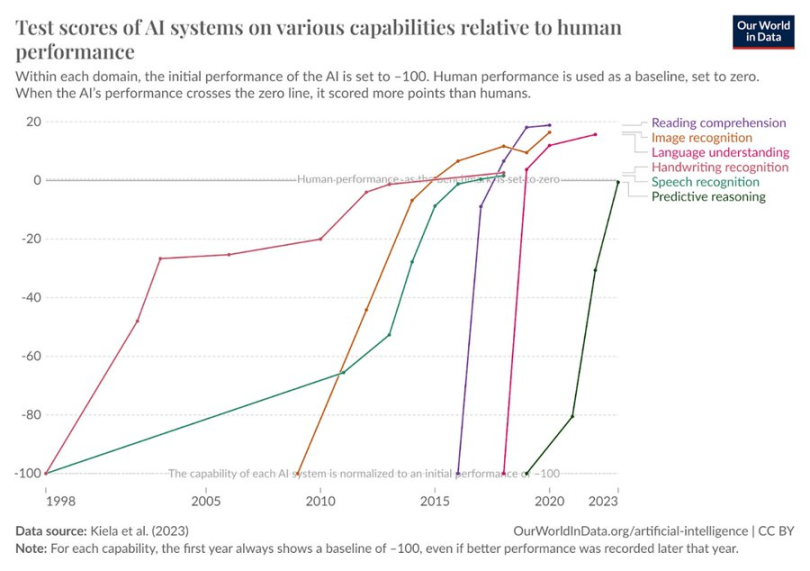
AI test scores on various dimensions of human behavior have increased
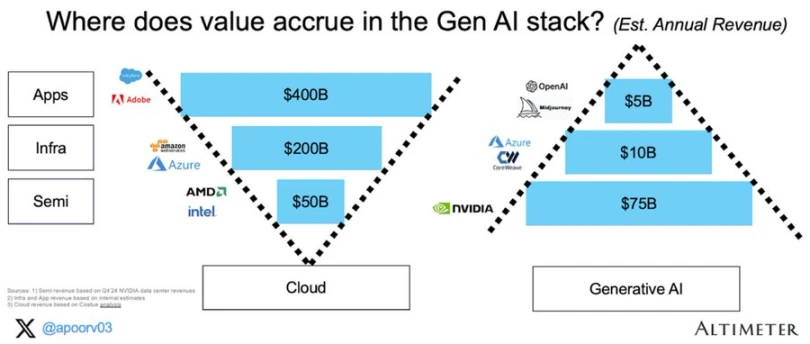
It seems logical that these agents leverage open, permissionless infrastructure—across payments and composable computing—to achieve more complex end goals. In the coming networked smart economy, economic flows may no longer be B -> B -> C, but user -> agent -> computing network -> agent -> user. The end result of this flow is the proxy protocol. Application or service-oriented enterprises have limited overhead and mainly run on-chain resources. The cost of meeting the needs of end users (or each other) in a composable network is much lower than that of traditional enterprises. Just as the application layer of Web2 captures most of the value, I am also a supporter of the fat proxy protocol theory in DeAI. Over time, value capture should shift to the upper layers of the stack.
Value Accumulation in Generative AI
The next Google, Facebook and Blackrock may well be proxy protocols, and the components to implement them are already being created.
DeAI Endgame
AI will change our economy. Today, the market expects that this value capture will be limited to a few large companies on the west coast of North America. DeAI represents a different vision. An open, composable vision of an intelligent network with rewards and compensation for even the smallest contributions, and more collective ownership/management.
While some of DeAI’s claims are overblown, and many projects are trading at prices significantly higher than their current actual momentum, the scale of the opportunity is significant. For those with the patience and foresight, DeAI’s ultimate vision of truly composable computing may justify blockchain itself.
This article is sourced from the internet: Delphi Digital: In-depth analysis of the opportunities and challenges of DeAI
Related: Is the popular Polymarket a good forecasting tool?
Original article by Felipe Montealegre Original translation: Luffy, Foresight News Once, a friend and I were discussing Robert Kennedys endorsement of Trump, and one participant confidently declared that Trumps chances of winning had increased by 2% because Polymarket predicted so. This was a good observation because the event happened quickly and there wasnt much other news to move the market. If Polymarket was an efficient market, this statement would seem to be tenable. The problem is that Polymarket is still an inefficient emerging market that cannot predict small changes in the probability of an event ( The way efficient markets work is that a large number of investors trade based on events. If you think Robert Kennedys endorsement will increase Trumps odds by 10%, you will buy with leverage to…