Arbitrage trading, the hidden driving force behind the boom in the crypto market
Original article by: Chi Anh , Ryan Yoon Yoon Lee
Original translation: TechFlow
Summary of key points:
-
Carry trading in finance and cryptocurrencies: Carry trading involves borrowing low-interest currencies to invest in high-yield assets. This strategy is widely used in traditional and crypto markets, allowing traders to drive liquidity and influence currency valuations. In the cryptocurrency space, this is often manifested in borrowing stablecoins to invest in decentralized finance (DeFi), which, despite high returns, comes with significant risks due to volatility.
-
Market dynamics and risks: Carry trading can enhance market liquidity, but it can lead to sharp fluctuations and increase market instability in times of crisis. In the crypto market, this can lead to speculative bubbles. Therefore, risk management is crucial for investors and companies using this strategy.
-
Future Trends and Challenges: Innovations such as yield tokenization and decentralized liquidity are shaping the future of arbitrage trading in cryptocurrencies. However, the potential rise of anti-arbitrage mechanisms poses challenges that require the development of more resilient financial products to address.
1. The impact of arbitrage trading on the market
The carry trade is a fundamental strategy in global finance whereby investors borrow in a low-interest currency and invest in a higher-yielding asset. The core objective is to profit from interest rate differentials, which can be significant depending on the currencies and assets involved.
An example of an arbitrage trade in traditional markets
Source: Jefferies Co, Tiger Research
For example, an investor can borrow Japanese yen at about 0.1% and invest in Mexican bonds yielding about 6.5%, earning about 5% without using their own capital. Carry traders provide liquidity by lending and investing between different markets, which helps price discovery and financial market stability.
However, this liquidity provision also comes with risks, especially when market conditions change unexpectedly, such as a financial crisis or a sudden adjustment in monetary policy. In times of market stress, such as the 2008 global financial crisis , carry trades can quickly collapse, causing a sharp reversal in currency values and significant losses for investors.
Carry trades can be very profitable when foreign exchange rates are stable. But when markets are volatile, these trades can be quickly closed. In such situations, investors often rush to sell risky assets and buy back borrowed currencies, leading to sharp market corrections. This chain reaction can exacerbate market volatility. Massive sell-offs increase market volatility and trigger a vicious cycle of falling asset prices and forced liquidations.
2. How arbitrage trading applies to the cryptocurrency market
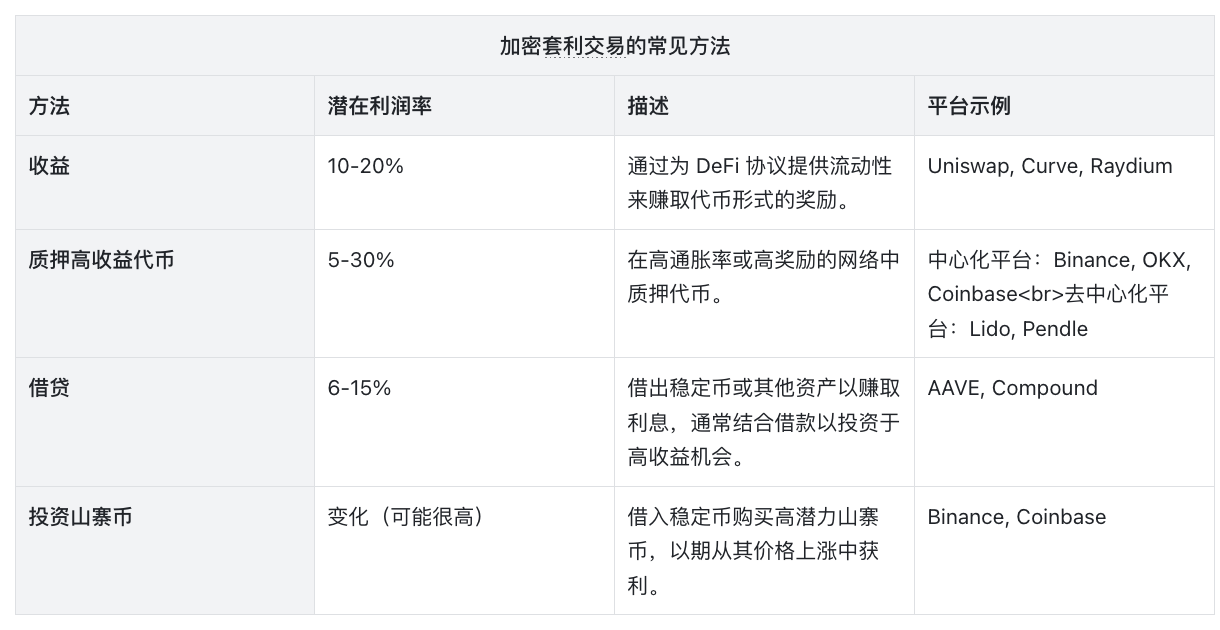
The numbers shown in the table are averages derived from multiple platforms. Actual numbers may vary depending on factors such as market conditions, the specific operations of the platform, and when the data was collected. Readers are advised to verify current data and conduct independent research before making decisions based on this information.
Table: Tiger Research, created using Datawrapper
The concept of arbitrage trading also has a significant impact in the cryptocurrency market.
A typical strategy is to borrow USDT at an annual yield (APY) of 5.7% and then invest in a DeFi protocol that offers a 16% yield. This can bring a profit margin of about 10% if the asset value is stable. Compared to the approximately 6% yield on Mexican bonds, the profit margin is usually higher due to the volatility of cryptocurrencies.
According to AAVE data, current lending rates show that stablecoins have become central to cryptocurrency arbitrage trading because they provide stable and low-cost borrowing options. For example, DeFi protocols in 2021 offer annual yields of more than 20%, making stablecoins an ideal low-cost borrowing tool for arbitrage traders.
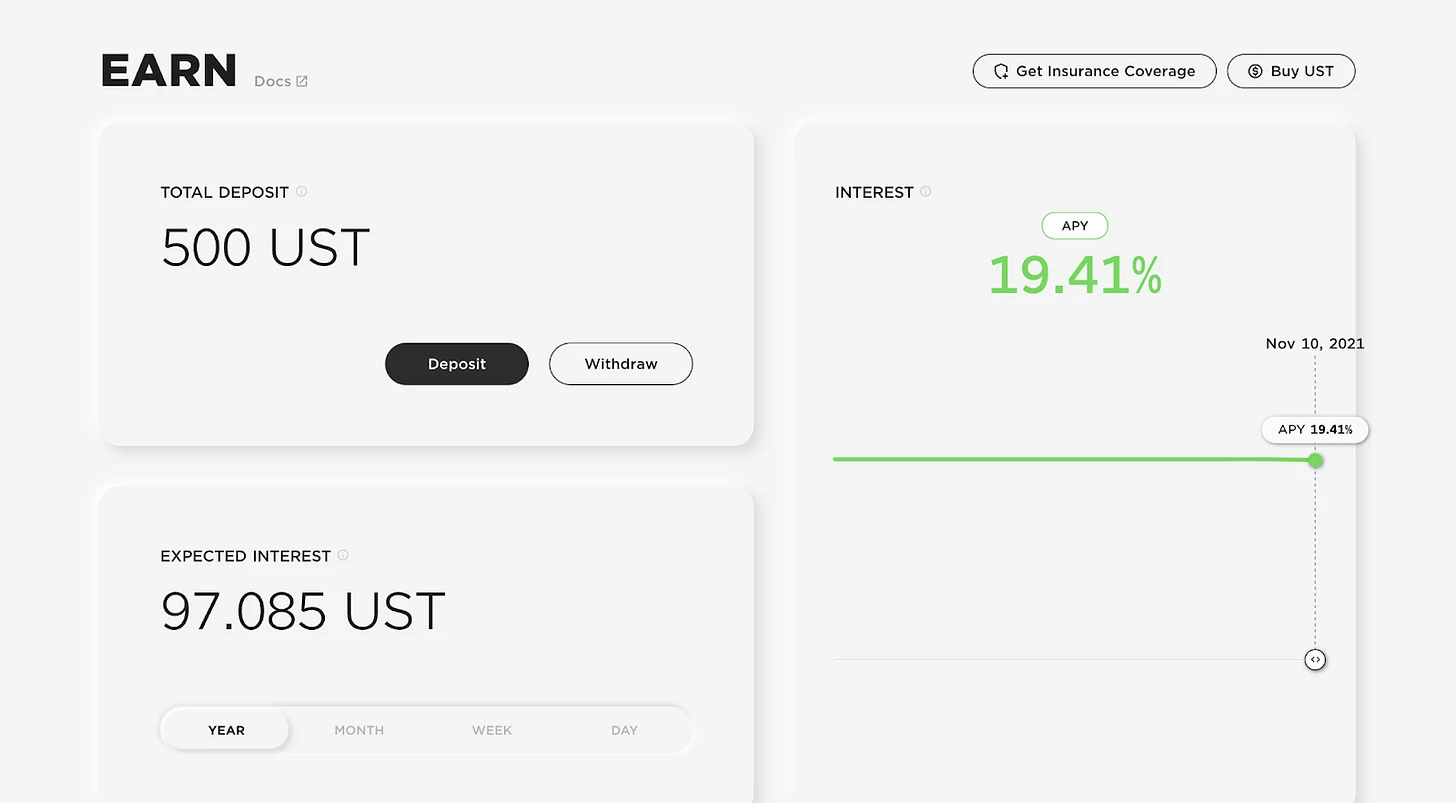
In 2022, Anchor Protocol offered a fixed 20% annual yield on UST. However, the market is not without risk. The collapse of the Terra/Luna ecosystem in 2022 is a warning. Many arbitrage traders borrowed stablecoins to invest in Terras Anchor Protocol, which promised up to 20% returns. However, when the value of $LUNA fell rapidly, these arbitrage trades were forced to close their positions quickly, resulting in large-scale liquidations and significant losses in the market.
The example reveals the inherent risks of carry trades in the cryptocurrency space, where borrowing stablecoins to invest in higher-yielding assets has become a common strategy. The volatility of crypto assets can amplify the impact of these trades to a degree rarely seen in traditional finance.
At the same time, this challenge also brings important opportunities. The market has the potential to develop innovative financial products and services that are suitable for the needs of cryptocurrency arbitrage trading, such as advanced risk management tools and yield optimization platforms. However, companies must adopt flexible strategies and respond quickly to market fluctuations to cope with the high volatility of crypto assets.
3. What are the differences between traditional arbitrage strategies and cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies?
Source: Tiger Research, created with Datawrapper
Although both traditional and cryptocurrency arbitrage trading are based on interest rate differentials, they differ significantly in terms of investor type, target assets, and risk level. Traditional arbitrage trading is typically the domain of institutional investors, such as funds and financial institutions, while cryptocurrency arbitrage trading provides opportunities for retail investors.
In terms of assets, traditional carry trading focuses on currency pairs in regulated markets, generally offering stable returns and moderate risk. In contrast, cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies utilize a wider variety of platforms, offering greater flexibility and higher potential returns, but also significantly increased risk. The use of leverage, yield farming, and staking rewards increases the complexity of cryptocurrency arbitrage trading, making it a profitable but riskier investment strategy.
In the rapidly changing cryptocurrency markets, policymakers must carefully weigh these factors when considering arbitrage trading.
4. What impact does arbitrage trading have on the cryptocurrency market?
4.1. Self-reinforcing mechanism and market momentum
Carry trades form a self-reinforcing mechanism that drives the market higher. As mentioned earlier, carry trades are when borrowers take advantage of low-interest assets to invest in high-yield opportunities. When the market outlook is positive, this can set off a cycle: rising prices attract more traders, further increasing the profitability of trades, as shown by:
-
More investors borrow stablecoins to invest in the market to make profits.
-
The increase in stablecoin lending has pushed up market prices.
-
As prices rise, more investors join in, creating a self-reinforcing cycle.
However, this cycle poses significant risks in the volatile cryptocurrency market. Sudden changes in the market鈥攕uch as a drop in the value of the investment asset or a surge in borrowing costs鈥攃an lead to the rapid unwinding of these trades. Such large-scale withdrawals can cause liquidity problems and sharp price drops, further increasing market instability. While carry trades can increase liquidity and generate returns, they can also cause sudden and severe market turmoil.
4.2. Improving the liquidity of the cryptocurrency market
In the DeFi summer of 2021, DeFi鈥檚 total locked value (TVL) achieved significant growth
Source: DeFiLlama
Cryptocurrency arbitrage trading, especially those involving stablecoins, has significantly enhanced market liquidity. Stablecoins such as USDT, USDC, and DAI are often used in arbitrage trading, providing the necessary liquidity for DeFi platforms (including lending protocols). This influx of funds facilitates smooth transactions and improves the efficiency of price discovery, thus benefiting the entire cryptocurrency market.
In 2023, the average daily trading volume of stablecoins exceeded $80 billion, showing their important role in maintaining liquidity in the crypto market. In addition, the increase in liquidity attracts institutional investors, who generally prefer markets with higher liquidity. This in turn brings more capital inflows and promotes market stability.
5. New trends in arbitrage trading
5.1. The rise of income tokens
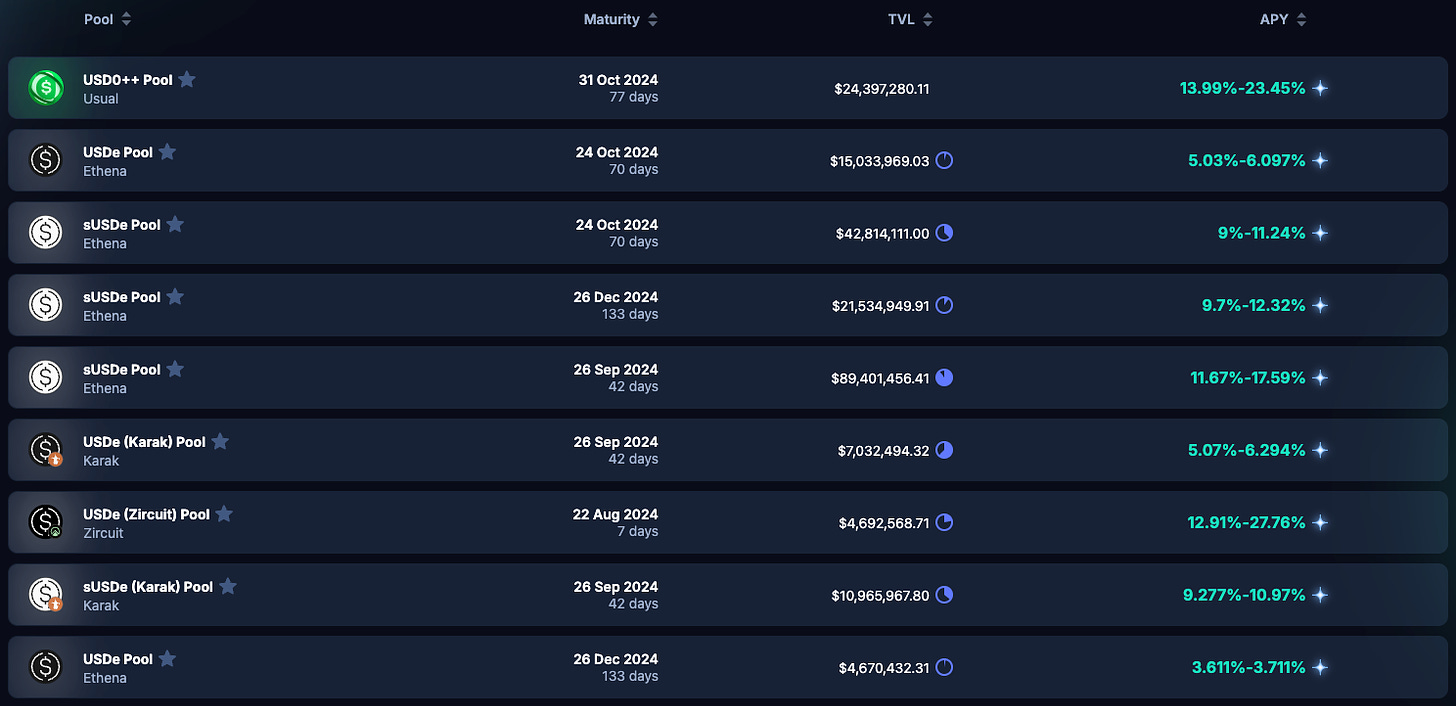
Annual yield (APY) of stablecoins on the Pendle protocol. Source: Pendle
As the crypto market continues to evolve, new trends are emerging in arbitrage trading. One of these trends is yield tokens, where investors can trade future earnings separately from their principal on platforms such as Pendle. This innovation makes more complex arbitrage strategies possible, allowing investors to hedge or speculate on future earnings.
5.2. Possibility of anti-arbitrage mechanisms in crypto markets
Anti-arbitrage mechanisms refer to situations where the market expects future volatility to exceed current levels. This poses specific challenges to crypto markets, especially for carry trades. When price volatility increases, carry trades become less efficient because they typically involve borrowing low-interest assets to invest in high-yield assets. As liquidity costs rise and the risks associated with leverage increase, this strategy can become not only less profitable, but also dangerous.
However, due to their deflationary nature (i.e. limited supply) crypto assets like Bitcoin may excel in an anti-carry environment. Fiat currencies are susceptible to inflation, while Bitcoin and similar crypto assets can serve as a store of value and a hedge against the depreciation of traditional investments. In such a context, they may become a powerful alternative to traditional carry trade strategies.
6. Conclusion
Arbitrage trading has always been a key driver of global finance, and its application in the crypto market marks a significant evolution of this strategy. In the future, arbitrage trading will develop amid innovation, regulatory changes, and the continued interaction between traditional and crypto markets. As more and more crypto ETFs enter the market, the boundaries between traditional and digital finance are becoming increasingly blurred, providing institutional investors with opportunities to enter the crypto market to earn high returns. This change may attract capital inflows from the traditional financial sector, further enhancing the legitimacy of the crypto market and expanding its influence.
However, businesses and investors in the crypto space need to carefully balance the risks and rewards of arbitrage strategies and keep a close eye on emerging trends that could reshape the market landscape. The possibility of anti-arbitrage mechanisms due to regulatory changes or shifts in market dynamics increases the complexity of the market. This complexity will challenge traditional approaches while also providing new opportunities for participants who are flexible. By identifying these changing trends and remaining flexible, market participants can better seize the unique opportunities presented by the convergence of traditional finance and crypto finance.
This article is sourced from the internet: Arbitrage trading, the hidden driving force behind the boom in the crypto market
Related: Advanced Formal Verification of Zero-Knowledge Proofs: How to Prove Zero-Knowledge Memory
In our blog series on advanced formal verification of zero-knowledge proofs , we have discussed how to verify ZK instructions and a deep dive into two ZK vulnerabilities . By formally verifying every zkWasm instruction, we found and fixed every single vulnerability, allowing us to fully verify the technical safety and correctness of the entire zkWasm circuit, as shown in the public report and code repository . Although we have shown the process of verifying a zkWasm instruction and introduced the initial concepts of the project, readers familiar with formal verification may be interested in understanding the uniqueness of zkVM compared to other smaller ZK systems or other types of bytecode VMs in verification. In this article, we will discuss in depth some technical points encountered when verifying the zkWasm…