Crypto Tax Policy in Asia at a Glance: Which Countries Are More Friendlier?
Original author: Ryan Yoon, Yoon Lee, Tiger Research
原文翻譯:魯夫、前瞻新聞
概括
-
Tax policies take many forms, including tax exemption, progressive tax, flat tax, transitional tax and transaction-based tax. Different tax forms reflect the economic strategies and policy priorities of various countries.
-
The government wants to ensure tax revenue, while investors are worried about high taxes. The conflict between the two has led to capital outflows to overseas exchanges.
-
為了 加密貨幣currency tax policies to be successful, policymakers need to balance tax revenue generation with supporting the healthy development of the crypto market.
1. Cryptocurrency trading and taxation
Taxation of cryptocurrency transactions has been a hotly debated topic since the emergence of the cryptocurrency trading market. The core conflict lies in the different priorities of the government and investors. The government emphasizes the need to ensure taxation, while investors worry that excessive taxation will Leading to decreased profitability.
However, taxation is an inevitable component of modern social systems and a key driver of market development. In particular, cryptocurrency taxation is expected to lay the foundation for market growth through three key effects.
First, it can establish a formal market. The example of the stock market shows that taxing profits or transactions represents official recognition of the relevant assets, which can help to establish a stable foundation for crypto market activities.
Second, it can strengthen investor protection. The U.S. Consumer Financial Protection Act and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) established in 2010 are examples of protecting investors through regulation. In the Web3 market, restricting undifferentiated products Publication and misleading advertising helps prevent fraud and protect the rights of investors.
Finally, taxation can accelerate the integration of cryptocurrencies into the existing financial system by clarifying their legal status. Such integration can increase market stability and trust.
However, given the uniqueness of the cryptocurrency market, it is difficult to expect taxation to have a positive effect based solely on experience in the stock market. Given the rapid growth of cryptocurrencies, many current tax systems have been criticized as a pure means of extracting value. This has led to governments and Conflicts among investors are intensifying.
In this context, this report will examine the cryptocurrency taxation systems of major Asian countries and analyze how the three effects mentioned above are achieved: market establishment, investor protection, and system integration, in order to provide a balanced approach for investors and governments. Perspective.
2. Comparative analysis of cryptocurrency taxation in major Asian countries
An analysis of the cryptocurrency tax systems of major Asian countries reveals five different policy types. These differences reflect each country’s economic structure and policy priorities.
For example, Singapore is exempt from capital gains tax and only imposes a 17% income tax when cryptocurrencies are recognized as business income. This flexible approach has solidified Singapores position as a global cryptocurrency hub. Similarly, Hong Kong is considering a new regulation for hedge funds. The tax exemption policy for investment income of family offices further enhances their attractiveness to institutional investors.
In contrast, Japan imposes a high tax rate of up to 55%, with a focus on curbing speculative activities. However, Japan is also considering a proposal to reduce the tax rate to 20%, which may indicate that Japan may change its current approach to crypto taxation.
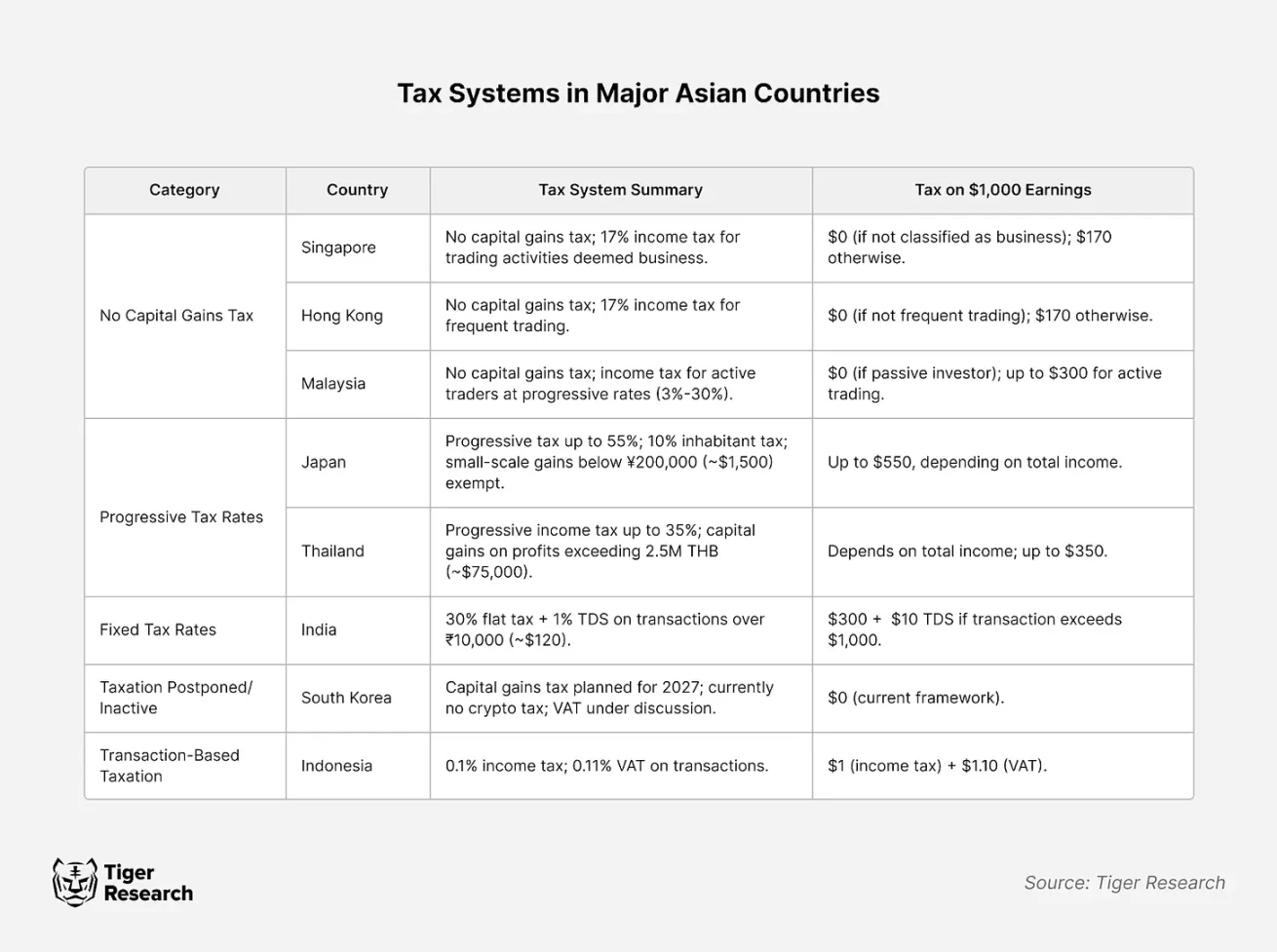
2.1 Duty-free countries: Singapore, Hong Kong, Malaysia
Major Asian financial centers such as Singapore, Hong Kong and Malaysia have all adopted a capital gains tax exemption policy for cryptocurrencies, which is in line with the long-standing economic strategies of various countries.
These countries’ tax-free policies are consistent with their traditional financial frameworks. Historically, they have attracted global capital through low tax rates. Maintaining this stance on cryptocurrencies demonstrates policy consistency and a clear commitment to their economic principles.
This strategy has yielded significant results. For example, Singapore became Asia’s largest cryptocurrency trading center in 2021. As there is no tax burden on investment profits, investors are actively participating in the market, accelerating its growth.
However, tax exemptions are not without their limitations. The main challenges include the risk of overheated speculation and reduced direct tax revenues for governments. These countries are taking alternative measures to address these issues. They are securing indirect tax revenues through the development of the financial services sector and through the regulation of exchanges. and strict supervision of financial institutions to maintain market stability.
2.2 Countries with progressive tax systems: Japan and Thailand
Japan and Thailand have high progressive tax rates on cryptocurrency trading profits. This policy reflects the broader social goal of wealth redistribution by taxing high-income groups. In Japan, the top tax rate is 55%, which is comparable to traditional financial assets. The policies are consistent.
However, such a high tax rate also has considerable drawbacks. The most notable problem is capital flight, where investors move assets to tax-free areas such as Singapore, Hong Kong or Dubai. There are also concerns that the heavy tax burden may suppress the market. increase.
2.3 Uniform tax rate countries: India

Source: ISH News Youtube
India imposes a flat tax rate of 30% on profits from cryptocurrency trading. This approach differs from the progressive taxation system used in traditional financial markets and reflects a strategic choice aimed at achieving two key goals: administrative efficiency and market transparency.
Indias flat tax policy has produced several significant results. First, the tax system is simple and clear, reducing the administrative burden on taxpayers and tax authorities. In addition, the same tax rate is applied to all transactions, minimizing tax avoidance strategies.
However, a flat tax system also has obvious limitations. The biggest concern is that it could discourage small investors from entering the market. Even small profits are subject to a high tax rate of 30%, which would be a heavy burden for small investors. In addition, imposing the same tax rate on high-income and low-income groups also raises questions about tax fairness.
The Indian government is aware of these issues and is currently exploring solutions. Proposed measures include reducing tax rates for small transactions and providing incentives for long-term holders. These efforts aim to retain the benefits of a unified tax system while promoting stable market growth.
2.4 Transitional approach: South Korea

Source: Kyunghyang News
South Korea has adopted a cautious approach to cryptocurrency taxation, reflecting the high uncertainty of the cryptocurrency market. A clear example is that the financial investment income tax originally scheduled to be implemented in 2021 has been postponed to 2025. The implementation of cryptocurrency taxation is also in accordance with The same idea was further postponed to 2027.
This transitional approach has clear advantages. It allows the market to grow organically while providing time to observe policy outcomes in other countries and global regulatory trends. By studying the cases of Japan and Singapore, South Korea aims to establish an optimized tax framework ex post facto.
But there are challenges with this approach. The lack of a clear tax system could create market confusion and increase the risk of speculative overheating. In addition, investor protection could be compromised by the lack of regulatory infrastructure, hampering long-term market development.
2.5 Transaction-based taxation: Indonesia
Unlike other Asian countries, Indonesia has implemented a unique transaction-based tax system. The system imposes 0.1% income tax and 0.11% value-added tax (VAT) on transactions. The policy was introduced in May 2022 as part of Indonesia’s wider Part of the financial market modernization reform.
The transaction tax improves market transparency by applying a low, uniform tax rate to all transactions, streamlining procedures and encouraging investors to use licensed exchanges. Since its implementation, trading volumes on licensed exchanges have increased significantly.
But the policy has its limits. Similar to India, the flat tax rate places an undue burden on small investors. For frequent traders, the cumulative tax costs can be very high, raising concerns about reduced market liquidity. Worry.
The Indonesian government is aware of these challenges and plans to refine its policies based on market feedback. Measures under consideration include tax cuts for small transactions and incentives for long-term investment. These adjustments are intended to retain the advantages of a transaction-based tax system while addressing its shortcomings. Place.
3. Conflict between investors and governments
Although tax systems vary from country to country, conflicts between governments and investors over cryptocurrency taxation remain a common problem. These conflicts arise not only from taxation practices, but also from fundamental differences in the perception of crypto assets. The nature of the conflict varies according to the tax policies of each country.
Governments around the world see profits from cryptocurrency trading as a new source of tax revenue. In particular, as the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated fiscal 去中心化金融cits, the rapid growth of the cryptocurrency market has become an attractive source of stable income. For example, Japan’s progressive tax system levies The high tax rate of 55% and Indias flat tax rate of 30% both highlight the governments strong need for tax revenue.

Source: GMB Labs
From an investors perspective, excessive taxation is an obstacle to market growth. Compared with traditional financial products, higher tax rates, coupled with the cumulative tax burden caused by frequent transactions, have hindered investment activities. As a result, capital flight has Many investors are moving their assets to offshore platforms or tax-free jurisdictions such as Singapore and Hong Kong. This suggests that the governments efforts to ensure tax collection may be counterproductive.
In some cases, the government only focuses on taxation and fails to introduce policies to support market development, which further exacerbates the contradictions.
Finding a new balance between governments and investors is becoming increasingly important. The solution requires more than simple tax adjustments, it requires governments to develop innovative policies that support healthy market growth while ensuring appropriate tax revenues. This balance will be a key policy challenge for governments in the coming years.
4. 市場 revitalization policies at the national level
Cryptocurrency taxation has a dual impact on market development. While some countries use it as an opportunity for institutionalization and market growth, others face market stagnation and brain drain due to strict tax policies.
Singapore is a great example of a successful market activation. Singapore encourages innovation by exempting capital gains tax, through systemic support for blockchain companies and regulatory sandbox. This comprehensive approach has solidified its position as Asia’s cryptocurrency hub.
Hong Kong is also implementing an active market development strategy. While maintaining its tax exemption policy for individual investors, Hong Kong is expanding the licensing framework for crypto asset management companies. Notably, from 2024, Hong Kong will allow qualified institutional investors to invest in crypto assets. Currency ETF trading further expands market participation.
On the other hand, strict tax policies in some countries have also become an obstacle to market growth. High tax rates and complex regulations force investors to transfer assets overseas, leading to the outflow of innovative companies and professional talents.
Ultimately, the success of cryptocurrency tax policies depends on a balance with market development. In addition to simply securing short-term tax revenues, governments must also consider how to foster a healthy and sustainable market ecosystem. Looking ahead, countries need to continuously adjust policies to Achieving this critical balance.
5. 結論
Taxing cryptocurrencies is an inevitable step in developing the crypto asset market. However, the stabilizing effect of taxation needs to be carefully reconsidered. Some people believe that transaction taxes can curb speculative trading and reduce market volatility, but historical cases show that this effect is often not achieved. .
A typical example is Sweden in 1986. At that time, when the financial transaction tax was increased by 100 basis points, a large part of stock trading shifted to the UK market. Specifically, 60% of the trading volume of 11 major Swedish stocks shifted to the London market. , highlighting the consequences of ineffective tax policies.
Both the government and investors must carefully assess the actual impact of taxation. The government should not only focus on simple tax revenue, but also on fostering a sustainable and healthy market environment. Investors should view taxation as a way to institutionalize the market. opportunities to promote a more stable and mature investment environment.
Ultimately, the success of cryptocurrency taxation depends on whether governments and market participants can find a way to strike a balance between them. This is not just a matter of adjusting the tax rate, but a key challenge that will determine the success of the crypto asset market. Long-term direction and development.
This article is sourced from the internet: Crypto Tax Policy in Asia at a Glance: Which Countries Are More Friendlier?
According to incomplete statistics from Odaily Planet Daily, there were 20 blockchain financing events announced at home and abroad from December 2 to December 8, which was a decrease from last weeks data (21). The total amount of financing disclosed was approximately US$218 million, which was an increase from last weeks data (US$173 million). Last week, the project that received the most investment was the multi-asset investment platform Public ($135 million); followed by the ZK-driven interoperability protocol Union ($12 million). The following are specific financing events (Note: 1. Sort by the amount of money announced; 2. Excludes fund raising and MA events; 3. * indicates a traditional company whose business involves blockchain): Multi-asset investment platform Public completes $135 million D-2 round of financing, led by Accel On December 3, multi-asset…







