Decoding funding rate arbitrage: How to obtain stable annualized returns through spot and perpetual hedging?
原作者: 黑天鵝
原文翻譯:TechFlow
在 加密貨幣 perpetual contract market, price deviations often occur, and traders can take advantage of these price errors to profit from them.
Cash and Carry Trade is a classic profit-making strategy that allows traders to earn profits from the difference between the perpetual contract price and the spot price.
Funding rate arbitrage – Earn 25% -50% passive income every year through spot and futures arbitrage strategies?
In the crypto perpetual contract market, price deviations often occur, and traders can take advantage of these price errors to profit from them. Spot and futures arbitrage is a classic strategy that specifically targets the difference between perpetual contracts and spot prices, allowing traders to easily make profits.
This strategy allows traders to arbitrage on centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX) without incurring high fees. Specifically, you can establish a spot long position on an asset and sell the corresponding futures derivative at the same time. When the market as a whole tends to be long (i.e. the price premium is high), you can get additional income through funding rates. If you think this sounds a bit complicated, dont worry, I will explain it to you in detail using ELI 5 (easy to understand way).
What is the funding rate?
Funding rate is a periodic fee that traders need to pay or receive based on the difference between the perpetual contract price and the spot market price. The size of this rate depends on the skew of the perpetual contract market and the degree of deviation of the perpetual contract price from the spot market.
In simple terms, when the perpetual swap contract is trading at a higher price than the spot price (i.e., a premium), the deviation on trading platforms such as Binance, Bybit, dYdX, or Hyperliquid will become positive, and long traders will need to pay funding rates to short traders. Conversely, when the perpetual swap contract is trading at a lower price than the spot price (i.e., a discount), the deviation will become negative, and short traders will need to pay funding rates to long traders.
What we are going to do is basically imitate the operation method of Ethena Labs: long ETH spot and short ETH perpetual contract. But the difference is that we will do it ourselves and choose the asset we are interested in (hint: it is not necessary to choose ETH).
If you dont want to read the previous content, I will try to explain it to you in a simple way.
Let’s say we take Ethereum as an example and we want to go long on ETH (preferably staked ETH).
We can take stETH (3.6% annualized yield) as an example, while shorting $ETH on the perpetual contract market (for example on Binance or Bybit).
When we are long and short equal amounts of ETH at the same time, our portfolio is “Delta Neutral”. This means that no matter how the price of ETH fluctuates, we will not lose or gain due to price changes.
The Delta Neutral Strategy is an investment method that hedges against the risk of market price fluctuations by balancing long and short positions. For example, if I open a long position of 1 ETH and a short position of 1 ETH at the same price, then no matter how the market price changes, the total value of my portfolio will not be affected (ignoring fees).
In this strategy, our income comes from two parts: ETH staking income and funding rate income.
Funding rate is a mechanism used to adjust the difference between perpetual contract price and spot market price. It acts like the interest cost in spot margin trading, and ensures that the price of perpetual contract does not deviate from the spot market price by adjusting the capital flow between long and short parties.
The settlement method of funding rate is as follows:
-
Funding is a fee that is settled directly between buyers and sellers, usually at the end of each funding interval. For example, with an 8-hour funding interval, funding will be settled at 12:00 AM, 8:00 AM, and 4:00 PM UTC.
-
On decentralized exchanges such as dYdX and Hyperliquid, funding fees are settled every hour, while Binance and Bybit settle every 8 hours.
-
When the funding rate is positive, long positions pay funding to short positions; when the funding rate is negative, short positions pay funding to long positions (this usually happens in a bull market, which I will explain in detail later).
-
Only traders who still hold positions at the time of fund settlement will pay or receive funding fees. If you close your position before the funds are settled, no funding fees will be incurred.
-
If the traders account balance is insufficient to pay the funding fee, the system will deduct it from the position margin, which will cause the liquidation price to be closer to the mark price, thereby increasing the liquidation risk.
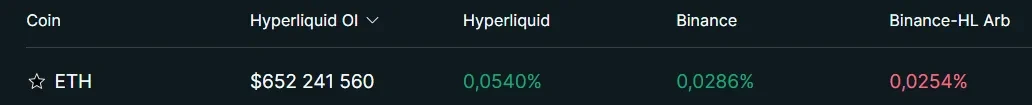
Lets analyze the funding rate shown in the picture. The funding rate calculation mechanism adopted by perpetual contract exchanges on different chains may be slightly different, but as a trader, you need to understand the time period of funding payment/receipt, and how the funding rate fluctuates over time. Here is how to calculate the annualized rate of return (APR) based on the funding rate in the picture:
For Hyperliquid:
0.0540% * 3 = 0.162% (1-day APR)
0.162% * 365 = 59.3% (1-year APR)
As you can see, Binance has a lower funding rate and an annualized rate of return of 31.2% (calculated in the same way). In addition, there is an arbitrage opportunity between Hyperliquid and Binance. You can go long on ETH perpetual contracts on Binance and short on ETH perpetual contracts on Hyperliquid, thereby obtaining the difference in annualized rates of return of 59.3% and 31.2%, or 28.1%. However, this strategy also has some risks:
-
Funding rate fluctuations may cause long funding fees on Binance to be higher than short funding fees on Hyperliquid, resulting in losses.
-
Because long positions are not spot, you cannot receive staking rewards, which will reduce overall returns.
However, the advantage of this method is that you can use leverage when using perpetual contracts for long and short operations, thereby improving the efficiency of capital use. It is recommended to make an Excel spreadsheet to compare the benefits and risks of different strategies and find the one that suits you best.
When the funding rate is positive (as in our example), long traders need to pay funding, while short traders receive funding. This is critical because it provides the basis for us to design a Delta Neutral strategy that exploits the funding rate to profit.
Spot and futures arbitrage
One of the simplest and most common strategies is “Cash and Carry Trade”, which is to buy spot assets and sell perpetual contracts with the same amount at the same time. Taking ETH as an example, the trading strategy is as follows:
-
Buy 10 ETH/stETH spot (worth $37,000)
-
Sell 10 ETH perpetual contract ($37,000 USD, available on dYdX, Hyperliquid, Binance or Bybit)
At the time of writing, ETH is trading around $3,700. To execute this strategy, traders need to try to complete both buy and sell operations at the same price and quantity to avoid unbalanced risk (i.e., market fluctuations that prevent the two positions from being fully hedged).
The goal of this strategy is to obtain an annualized return of 59% through the funding rate regardless of whether the market price rises or falls. However, although this return looks very attractive, traders need to be aware that the funding rate of different exchanges and different assets may vary, which will affect the final return.
Your daily funding income can be calculated using the following formula:
Funding income = Position value x Funding rate
We take the current ETH funding rate of 0.0321% as an example to calculate the daily income:
-
Daily funding income: 10 ETH x 3,700 = $37,000 x 0.0540% = $20, settled 3 times a day, totaling $60.
-
Daily staking income: 10 ETH x 1.036 = 0.36 ETH per year / 365 = 0.001 ETH per day, equivalent to $ 3,700 x 0.001 ETH = $ 3.7.
Therefore, the total daily profit is $60 + $3.7 = $63.7. For some, this may be a good profit, while for others, it may seem insignificant.
However, this strategy also faces some risks and challenges:
Difficulty of opening long/short orders at the same time: Check the spot price and perpetual contract price of ETH on Binance or Bybit, and you will find that there is usually a price difference between the two.
For example, as I write this article, the spot price is $3,852, while the perpetual contract price is $3,861, a spread of $9.
-
How do you do it? Try it with a small amount of money and you will find that it is almost impossible to perfectly match long and short positions.
-
Should you go long first and wait for the price to rise before going short, or go short first and wait for the spot price to fall before buying? Or should you balance your long and short positions by building positions in batches (DCA, i.e. buying or selling gradually in stages)?
Trading Fees: Both opening and closing a position incurs a fee. If you hold a position for less than 24 hours, the fees may cause you to lose money.
Rebalancing risk with low capital: If you have equal long and short positions, but the market moves drastically (e.g. ETH doubles to $7,600), your short position will suffer a deep loss while your long position will make a big profit. In this case, your account equity may be unbalanced or even forced to close your position.
Liquidation risk: Depending on the amount of funds you have available on the exchange, if your short position encounters extreme market conditions (such as a surge in ETH prices), liquidation may be triggered.
Funding rate fluctuations: Funding rates will fluctuate with market changes, which may directly affect your returns.
Difficulty in closing positions at the same time: The challenges faced when closing a position are similar to those when opening a position. It may not be possible to accurately match long and short positions, resulting in additional costs or risks.
Centralized exchange risk: If problems occur with Binance or Bybit, such as bankruptcy or withdrawal restrictions, your funds may be at risk of loss. This is similar to the risk of smart contract vulnerabilities in DeFi.
Risk of operational errors: If you are not familiar with perpetual contracts, you need to be especially careful. An operational error in a market order can lead to extreme price fluctuations, and you may be traded at a very bad price. In addition, opening or closing a position only requires the click of a button, and an operational error can greatly reduce the trading results.
By the way, you can also look into options trading. This method may be easier and save you some costs 🙂
I just wanted to show you how to try out Ethena Labs’ trading strategies.
That’s all for today.
See you in the order book, anonymous friend.
This article is sourced from the internet: Decoding funding rate arbitrage: How to obtain stable annualized returns through spot and perpetual hedging?
Related: Overview of the current status of Layer 2 technology development on Filecoin
Original author: Filecoin Network Layer 2 (L2) is an important innovation in blockchain technology that enhances the scalability, efficiency, and functionality of their respective networks. For Filecoin , L1 focuses on decentralized storage, and L2 solutions play a vital role in bringing new features to network infrastructure. As Filecoin continues to grow, L2 solutions are driving Filecoin to market and tailoring products for creators focused on specific verticals. This article explores the current state of L2 solutions on Filecoin, highlighting groundbreaking advances and future directions. Underlying Architecture Before diving into L2, it is recommended to first understand the shared framework on which Filecoin L2 is based: InterPlanetary Consensus (IPC). Video link: https://youtu.be/aRyj9kOvW7I Interstellar Consensus (IPC) is a framework designed to solve the scalability problem of decentralized applications (dApps). IPC does…









👋