Overview of the SVM track: MoveVM is implemented, how far can SVM go?
Orijinal|Odaily Planet Daily
Yazar: jk
As the demand for high performance and scalability becomes more urgent, Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) is gradually becoming an important part of promoting the development of the decentralized ecosystem. By combining Solanas speed with Ethereums ecological advantages, innovative projects based on SVM are creating a new experience for developers and users, breaking the performance bottleneck of traditional blockchain architecture.
Not long ago, the launch of Move gave us great expectations for the virtual machine track. After MoveVM, the first virtual machine hot spot was SVM.
This article will explore in depth three representative SVM projects – Sonic SVM, SOON and Eclipse . They have similarities in technical details but also great differences. Odaily Planet Daily has sorted out the public information of these three projects and interpreted them. Let us start with the first project – Sonic, which has just been TGE.
Sonic SVM: SVM for games may be the cradle of the next sheep-and-sheep
According to the official website, Sonic SVM is the first atomic SVM chain, designed to support the aggregation and settlement of the sovereign gaming economy on Solana.
Sonic SVM is built on top of Solanas first concurrent scaling framework, HyperGrid, and Sonic is the first Grid instance managed by the framework. Specifically, both HyperGrid and Sonic SVM come from the team behind Sonic (formerly Mirror World), which means that the team itself built both the framework and the product, similar to the relationship between Virtuals and Luna.
HyperGrid was designed to be highly customizable and scalable while maintaining native composability with Solana. According to the developer documentation, applications supported by HyperGrid can be written on EVM, but ultimately executed on Solana, with Solana as the final settlement layer, which is conducive to bringing EVM ecosystem applications to Solana. This is different from the direction of MoveVM technology, which uses Ethereum as the final settlement layer.
Another issue that needs to be noted is that Sonic SVM and the project of the same name Sonic (created by the Fantom team) are two completely different projects . Readers need to pay attention to the difference between projects and assets.
The teams vision is that Sonic was born to unlock new experiences for developers and players. We designed Sonic to be an incubator for high-performance decentralized games, in stark contrast to the traditional in-game asset trading experience.
According to the official website, the advantages of Sonic SVM mainly come from:
-
Extremely fast and low cost: Sonic uses SVM technology to provide players in all game-exclusive L1 chains with an ultra-fast on-chain gaming experience.
-
Atomic interoperability : Execute transactions on Sonic without redeploying Solana programs and accounts. Directly take advantage of Solana’s underlying services and liquidity.
-
Write for EVM, execute on SVM: Seamlessly deploy dApps from EVM chains to Solana through HyperGrid’s interpreter.
-
Composable game primitives and sandbox environment: Sonic provides native composable game primitives and extensible data types based on the ECS framework on the chain. Developers can use the game engine sandbox tool to build business logic on the chain.
-
Monetization Infrastructure: Sonic natively supports game growth, traffic, payment and settlement infrastructure to empower developers.
In terms of investors, Sonic is led by Bitkraft, and the total investor lineup is as follows:
Source: Sonic SVM official website
Problems and solutions
As a game infrastructure, Sonic SVM specifically addresses the underlying performance pressure of games running on Solana. The team’s own statement on this issue is:
From 2022 to 2023, the number of wallet accounts increased from 100,000 to 1 million, and is expected to exceed 5 million in 2024, and is expected to reach 50 million in the next few years. However, the explosive growth of dApp and DeFi activities is synchronized with the growth of users. The daily transaction volume increased from 4 million in 2022 to 200 million in 2024. It is conservatively estimated that it will exceed 4 billion by 2026, and may even reach tens of billions.
This growth trend has put Solana under tremendous performance pressure. Currently, the latency of its blockchain fluctuates between 6 and 80 seconds under the conditions of 2500-4000 TPS, and in most cases it remains at around 40 seconds. When TPS exceeds 4000, the transaction success rate drops to 70%-85%. As TPS may reach tens of thousands in the future, the performance bottleneck problem will become more prominent.
The situation is particularly severe in the gaming scenario. Full-chain games (FOCG), as well as highly concurrent small games and single large games, may bring instantaneous transaction peaks during special operation activities. This pressure not only affects the performance of the Solana main chain, but also directly affects the playability and user experience of the game. For the gaming industry, a poor user experience can be a fatal challenge.
To address these issues, Sonics innovative design focuses on the high concurrency and instantaneous transaction requirements in gaming scenarios , providing developers and players with a smooth and efficient on-chain experience.
Sonic x TikTok: What sparks will emerge from the diversion of large-scale Web2 applications?
SonicX is Sonics first TikTok Mini App and Sonics gaming platform on Tiktok. TikTok has more than 1 billion monthly active users, and what Sonic has to do is to select users who can directly enter the Web3 gaming world, and this process will be very similar to Telegram.
So how does Sonic do it specifically? First of all, users must have a real Tiktok account instead of a Douyin account to log in , which will directly bypass the countries and regions where Tiktok is not available. After that, these KYC-verified users can complete games and tasks through SonicX and interact with the underlying facilities of Sonic SVM. In general, the design of SonicX is not fundamentally different from most of the TG applets we can see, but because the user group comes directly from Tiktok, it saves the need for KYC and ensures that most users are real.
Source: SonicX
Then, a natural question arises: if most of the users come from the Web2 platform Tiktok, do they have to relearn Web3 knowledge when they enter SonicX? How do they know what a wallet is? What is a private key? This is precisely the most worthwhile aspect of SonicX to learn. Most of the operations in SonicX, except for the actual transfer of tokens to third-party wallets, are completely abstracted, and users are basically unaware of the existence of a wallet. From Sonics own Tap-to-Earn, to completing related tasks, to other games in the game center, SonicX automatically generates a wallet that is strongly bound to the users Tiktok account, without requiring any Web3 expertise to interact with the wallet. Even in the user center, you can see that the wallet avatars have been imported from Tiktok. In other words, in theory, this infrastructure can support complete account abstraction, and users do not need to understand the kripto industry until they need to sell their accounts or transfer game tokens out to sell on exchanges.
Sonic themselves put it this way in a blog post: “TikTok’s popularity among KYC-verified users provides us with unique insights into user preferences, creating a strong environment for Sonic games to gain traction. Through carefully designed user flows, we’ve paved an easy path for new Web3 players to explore and enjoy blockchain games, seamlessly integrating with their existing TikTok experience.”
Through simple login, incentives for on-chain operations to earn rewards, and a user-friendly onboarding process, SonicX has the potential to divert traffic through Tiktok. If there is any disadvantage, it is that the settings of SonicX itself and other games are still relatively simple, and there are no particularly eye-catching mechanisms and gameplay like the popular mini-programs. However, infrastructure is always the first step in the emergence of games, and diverting traffic through a Web2 is still the most likely prerequisite for the success of Web3 games.
This is also the direction in which Sonic SVM has the most unique advantage at present. Imagine that as a developer, after you develop a mobile game, you can seamlessly deploy it on Solana on the backend and on Tiktok on the frontend. If a video about this game goes viral, users can directly click into the game through the official account without registering a wallet, but the tokens in the game are all real on-chain tokens. So, is it possible that there will be the next on-chain version of the Jump Jump applet or Sheep? Will this be the mechanism for Web3 games to break out of the circle?
These are all easy questions to think of. What was unexpected was that they actually made a sheep-like game.
At the end of October 2024, Sonic SVM announced a strategic partnership with Mahjong Verse. Mahjong Verse, formerly Mahjong Meta, is also a veteran project in the Web3 gaming industry, backed by top investors such as Dragonfly and Folius. They made a replica of the game Sheep Out of Sheep on Sonic SVMs Tiktok, but the mechanism has changed to collecting three mahjong tiles to eliminate them. In other aspects, the levels are the same as Sheep Out of Sheep, with layers of mahjong tiles, requiring strong thinking skills and a little luck to pass.
This mahjong-themed game is also the first game on Sonic Applayer and can now be found in the Game Center of Sonic X. In Sonics announcement, it said, Integrating Mahjong Verse into our ecosystem not only demonstrates how our infrastructure supports complex gaming experiences, but also retains the ease of use that TikTok users expect. It can be seen that this is also the future vision of Sonic Applayer.
In summary, Sonic SVM focuses on the underlying infrastructure of games, and has clear application examples in the Tiktok Applayer. It has now reached the coin issuance stage. We are looking forward to what the next game released through Sonic SVM will look like, and whether it can break through the circle through the Tiktok traffic entrance.
Timeline
In June, Sonic announced the completion of a $12 million Series A financing round, led by Bitkraft Ventures, with participation from Galaxy Interactive, Big Brain Holdings, etc. It is reported that its fully diluted token valuation in this round of financing reached $100 million. Sonics legal entity Mirror World Labs has built a proprietary technology called HyperGrid Framework, which can achieve horizontal expansion through rollups on the Solana chain.
In September, Odaily reported that Sonic SVM recently announced the sales information of HyperFuse Guardian Nodes, which is said to be the first node sale in the Solana ecosystem.
The official announcement pointed out that HyperFuse Guardian Nodes are an integral part of the security and functionality of the Sonic Hypergrid framework in the SVM ecosystem. Node operators will help verify state transitions and improve network efficiency. Early adopters have the opportunity to buy Sonic tokens at a price lower than that offered to venture capitalists during Sonics $12 million Series A financing. This node sale is a key component of Sonics plan to develop the SVM ecosystem and the Solana gaming track. The company also revealed that it has cooperated with more than 40 game studios and has more than 2 million active wallets on the platform.
At the end of December, Sonic SVM announced that it would airdrop SONIC tokens to all users who joined its game on the Solana blockchain. The snapshot has not yet been taken and the airdrop will take place in January.
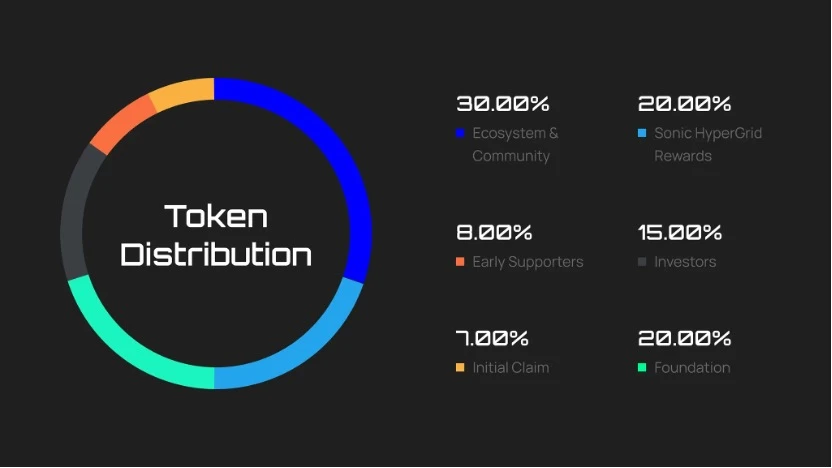
At the same time, Sonic SVM announced the token economics of its native token $SONIC. The total supply of SONIC is 2.4 billion, of which 57% is allocated to the community, including community and ecological development (30%), initial claims (7%) and HyperGrid rewards (20%).
Jetonomics of Sonic SVM. Source: X
On January 3, Sonic SVM announced on the X platform that the initial SONIC application will be open soon, aiming to reward supporters and contributors. The SONIC eligibility checker is now online, and users can check the initial application qualifications.
On January 7, Sonic SVM will officially launch TGE. Currently, the exchanges that have been confirmed to list the token include OKX, Upbit, Bybit, KuCoin, Backpack, etc.
SOON: A project without any VC involvement, the strongest execution layer on Ethereum
TPS above 30K , source: SOON official website
SOONs product is called Super Adoption Stack, which includes SOON Stack and SOON mainnet.
SOON Stack is a Rollup framework based on OP Stack and unique Decoupled SVM, designed to achieve maximum performance, supporting the deployment and operation of SVM Layer 2 on any underlying Layer 1. The chain deployed through SOON Stack is called SOON Chain . Currently, SOON Stack supports Ethereum as the settlement layer, Avail as the data availability (DA) layer, and integrates support from Caldera and Altlayer.
The SOON mainnet is the SOON chain deployed on Ethereum using the SOON Stack, aiming to become Ethereums most powerful L2.
InterSOON is a cross-chain messaging protocol designed to ensure smooth interaction between networks. It enables interoperability between SOON Mainnet, SOON Stack (SOON Chain) and other Layer 1 blockchains, connecting all networks together through a seamless interface. InterSOONs underlying cross-chain messaging is powered by Hyperlane.
SOONs core advantages
Currently, many projects with the theme of expansion are based on SVM, but SOON is unique in that it is an optimal SVM Rollup framework designed for efficient performance. By decoupling SVM and its TPU (transaction processing unit), SOON achieves real performance improvement and efficiency maximization.
Why did SOON choose decoupling instead of Forked SVM?
Limitations of Forked SVM:
-
Waste of Default Architecture: Many projects using SVM outside of Solana L1 are Forked SVM. This approach directly uses the existing Solana client and only adjusts some parameters, but does not modify the critical TPU or TVU (Transaction Verification Unit).
-
Data availability waste: The biggest problem with Forked SVM is the inefficient use of blobspace in the data availability (DA) layer. For example, even if there is only one ordering node, each block still generates voting transactions, which consumes a lot of resources.
SOON uses a customized decoupled SVM to optimize transaction processing efficiency and DA usage by removing voting transactions and peer-to-peer network overhead. Especially when no L1 consensus mechanism is required (such as Proof of History and Leader Schedule), the decoupled SVM can be optimized more flexibly.
Key benefits of decoupling:
-
Support for Fraud Proofs: The decoupled SVM provides L2 with native support for fraud proofs, which is core to the security of the L2 network. Fraud proofs ensure the security of the L2 state by verifying user transactions from L1 deposits (export pipelines) and L2 ordering nodes.
-
Improve performance and security: By optimizing transaction processing and DA usage, SOON Stack significantly reduces resource waste while enhancing network security to meet the high throughput and security requirements of Web3 applications.
The SOON team has analyzed decoupled SVM in detail in this blog post , which readers who are interested can read. (Original article in English)
SOONs Mission and Vision
SOON Stack aims to achieve the following goals:
-
Provide high-performance Rollup solutions in any L1 ecosystem.
-
Reduce transaction costs by 10 times.
-
Promote widespread adoption of SVM.
-
Unlock innovative application scenarios across ecosystems.
Targeted question: Why do we need a higher performance Rollup and technology stack?
The problem that the SOON team is targeting is completely different from that of Sonic SVM. The technology stack provided by SOON will eventually be settled on the Ethereum main chain, targeting the problem of insufficient performance of the Ethereum main chain. So, what are the problems they plan to solve? The following content is extracted and summarized from SOONs blog:
-
Single-thread bottleneck limits scalability: Most current Rollup frameworks still use a single-threaded operating environment, which has low processing efficiency and can easily lead to network congestion and high transaction fees during periods of high demand, seriously restricting the expansion potential of decentralized applications.
-
Gap in developer ecosystem : There is a clear gap between the dApp quality and developer capabilities of the EVM ecosystem and SVM. The SVM ecosystem attracts more high-level developers and develops high-quality products such as Jupiter through stronger engineering culture and tool support.
-
Liquidity fragmentation of EVM: The multi-chain phenomenon of the EVM ecosystem causes developers to repeatedly deploy the same products, resulting in reduced product quality and insufficient user appeal. The Solana ecosystem concentrates resources in a unified environment, significantly improving product and community experience.
-
Ethereum fee market problem: Ethereum’s global fee market mechanism causes high-demand transactions (such as NFTs) to drive up all transaction fees, limiting the economic viability of daily transactions. SVM’s localized fee market solves this problem by independently calculating fees to prevent unrelated transactions from affecting each other.
-
Complexity of zk-VM: Although zk-VM technology has potential in privacy and scalability, its high development threshold and high operating costs hinder its popularization, and it is difficult to achieve large-scale application in the short term.
-
Rusts advantages can help SVM: SVM uses Rust as the smart contract language, providing a higher performance and safer development environment. Compared with Solidity, it solves problems such as memory safety and concurrent processing, and is more suitable for high-performance blockchain application development.
-
Parallel processing improves network performance : EVMs sequential processing limits network throughput, while SVM uses parallel processing technology to process multiple transactions simultaneously, greatly improving network performance and ensuring fast response and low cost during high demand periods.
In other words, in a strict sense, Sonic SVM and SOON are just in the same SVM track, and they are not competitors. Sonic SVM targets the performance limitations of Solana, and the final settlement layer is Solana; while SOON will build L2 on the upper layer of Ethereum, targeting the performance bottleneck of Ethereum.
Ecological applications on SOON
Let’s remove all infrastructure applications and see what interesting toC applications there are on SOON. The biggest direction is in the DeFi direction;
SOONs official website displays six DeFi applications, most of which should be native DeFi applications. There are not many followers on the X platform, and their functions can meet most of the needs of the DeFi direction , including Portal Finance (lending agreement), Raptor (AMM), Alita (native DEX), and Sponge (staking). The other two are projects with a certain level of attention, namely:
EnzoFi, a cross-chain liquidity management center , has products including lending, bridge, staking and earning, etc. It also has its own points system. It is currently online on Solana, Sui, Eclipse, SOON and Movement, and the number of followers on the X platform has reached 163K .
Blendy is a more interesting project: it is a project that uses Meme coins and AI agent-related assets to provide currency market services . The collateral is all Meme coins, which is very consistent with the current hot spots. It is still in the testnet stage. The project announced on Twitter that the number of transactions has exceeded 150,000.
In terms of other applications that users can directly experience, there are four more interesting applications on SOON:
-
Aeronyx: Aeronyx is based on SOONs DePIN protocol, connecting millions of devices and tokenizing computing resources to promote the widespread use of distributed computing.
-
Gigentic: Gigentic is a collaborative platform based on SOON, where AI agents can work together and gain benefits through on-chain mechanisms, building a bridge for interaction between humans and AI.
-
CoindPay: CoindPay is a multi-functional payment and DeFi application that supports cross-industry payment scenarios based on SOON and provides users with efficient payment solutions.
-
Polyquest: Polyquest is a decentralized prediction market where users can predict events on the SOON platform and explore new models of prediction economy based on blockchain.
Timeline:
On August 27, according to The Block, Solana Optimistic Network (SOON for short) completed its co-builder round of financing. Solana Foundation Chairman Lily Liu, Solana Labs co-founder Anatoly Yakovenko, Coinbase Ventures Director Jonathan King, Celestia Labs co-founder Mustafa Al-Bassam, Avail co-founder Robinson Burkey, and Wormhole Foundation co-founder Robinson Burkey participated in the investment. The specific amount of financing has not been disclosed yet.
SOON co-builder round, source: SOON
This round of financing is exclusively for co-builders, and no venture capital firms participated. SOON only has news about this round of financing, which means that no venture capital funds have entered into SOONs total funds.
On November 8, SOON announced the official launch of the public testnet, which has a performance benchmark of 30,000 TPS and a block time of 50 milliseconds. SOON recommends that all Genesis hackathon participants migrate their projects to the new public testnet.
On January 3, SOON announced that the Alpha mainnet is now online and announced the SOON token economic model. The initial total supply of SOON is 1 billion (with an annual inflation of 3%), with the community allocation accounting for 51%, which will be distributed through a fair launch. In addition, the ecosystem allocation accounts for 25%, the airdrop and liquidity allocation accounts for 8%, the foundation/treasury allocation accounts for 6%, and the team and co-builder allocation accounts for 10%.
SOON Tokenomics, Source: SOON
SOON wrote in the blog post announcing the Alpha mainnet:
$SOON token distribution adopts a fair launch model: there are no pre-mined tokens, no pre-allocation to the team or private investors, and no special rights or opportunities for venture capital institutions. This distribution method is similar to the infrastructure token issuance in the ICO era of 2017, such as Solana, Polkadot, and Avalanche. Everyone can participate in the investment at the same time, and the vast majority of tokens will be allocated to builders and the community . More details will be announced next week, so stay tuned!
Eclipse: The earliest SVM to be launched, but no tokens were issued
Eclipse is a competitor of SOON and is also an SVM L2 released on Ethereum. From the official website, Eclipse is an L2 that focuses on research and ecosystem, and its design is also very stylish. In terms of stage, Eclipse is not lagging behind the two competitors mentioned above. The main network has actually been launched, but no tokens have been issued. It is unique in strategy and its overall position is closer to the Ethereum ecosystem, achieving the pure experience of Solana speed on Ethereum.
The introduction to Eclipse says,
Eclipse is Ethereums first Solana Virtual Machine (SVM)-based Layer 2, combining Solanas high speed with Ethereums liquidity. This innovative architecture provides users with a high-performance L2 solution that can leverage the rich liquidity of the Ethereum ecosystem while maintaining strict verifiability constraints. Through this design, Eclipse achieves a balance between performance and security, providing strong technical support for decentralized applications.
Eclipse uses Celestia as the DA.
One very obvious difference is that Eclipse did not issue its own tokens, but used Ethereum as the gas token for the entire L2, which is equivalent to tying itself firmly to the chariot of Ethereum. At the same time, Eclipse issued re-staked Ethereum tokens to drive L2.
Turbo ETH (tETH) is a unified restaking token (URT) launched by Eclipse in partnership with Nucleus, which aims to consolidate the most profitable protocols on Ethereum into a simple, easy-to-use default yield token. tETH provides users with a convenient way to earn restaking rewards while eliminating liquidity fragmentation and complexity.
Users can mint tETH through five types of Liquid Heavy Staking Tokens (LRT) deposits, including WETH, weETH, ezETH, rswETH, apxETH, and pufETH. The design of tETH not only disperses risks, but also maximizes user rewards through its unified yield mechanism, bringing a new liquidity management tool to on-chain users.
tETH is a token with exchange rate benefits, similar to Compound’s cTokens and Lido’s wstETH, where its ETH-based benefits increase the exchange rate over time, while non-ETH rewards can be claimed through a separate interface.
As of the date of this article, according to DeFiIlama data, the TVL of the entire Eclipse chain has reached 19.33 million US dollars, which is not very high. The number of followers of the X platform is 195,000.
Eclipse Ecosystem
In terms of the DeFi ecosystem, the largest DEX on Eclipse is Orca, with a current TVL of $9.2 million. The TVL of the second largest lending protocol Save is $3.55 million, and the TVL of the second largest DEX Invariant is $3.25 million. These data have all increased significantly in the past month.
Now let’s look at consumer applications. The following are the applications that have attracted a lot of attention on the X platform in the Eclipse ecosystem:
-
After School Club: an NFT series and Eclipse’s genesis NFT;
-
SEND Arcade, a platform where you can win ETH by playing games;
-
Dscvr.one, a social protocol, has about 80,000 followers on the X platform;
-
HedgeHog: A prediction market also on Solana;
-
AllDomains – Eclipse domain name service.
-
Moonlaunch.fun: Pump.fun on Eclipse;
-
Blobscriptions: Inscriptions on Eclipse.
Timeline:
In September 2022, Eclipse announced that it had completed $15 million in Pre-Seed and Seed rounds of financing at a valuation of over 100 million US dollars, of which $9 million in Seed round financing was jointly led by Tribe Capital and Tabiya, with participation from Caballeros Capital, Infinity Ventures Crypto, Soma Capital, Struck Capital and CoinList; the other $6 million was in Pre-Seed round financing, led by Polychain Capital, with participation from Tribe Capital, Tabiya, Galileo, Polygon Ventures, The House Fund and Accel. It is reported that Eclipse is responsible for developing a customizable Rollup provider, aiming to become a universal Layer 2 platform compatible with multiple L1 blockchains.
In February 2023, Eclipse launched SVM, a scaling solution around Solana, which allows applications to be compatible with Polygon. Through this solution, dApps built for the Solana blockchain can migrate or become multi-chain through Polygon SVM, which can open the door to communities using and building different blockchains.
In December 2023, the Eclipse testnet will be made public;
In March 2024, Eclipse Labs announced the completion of a $50 million Series A financing, led by Placeholder and Hack VC, with a total financing amount of $65 million. This round of financing also attracted participation from investors such as RockTree Capital, Polychain Capital, Delphi Digital, Maven 11, DBA, Apollo-managed funds, Fenbushi Capital, ParaFi Capital, and strategic investments from Flow Traders, GSR, Auros, and OKX Ventures. Many researchers and developers participated in its angel round investment, including Barnabé Monnot (Ethereum Foundation), John Adler (Celestia Labs), Austin Federa (Solana Foundation), ZachXBT, and Meltem Demirors.
In May 2024, Eclipse founder and CEO Neel Somani resigned due to sexual harassment rumors and was replaced by Vijay Chetty, who will be promoted from Chief Growth Officer and assume all responsibilities of CEO. Chetty has more than ten years of cryptocurrency native experience and has held leadership positions at Uniswap Labs, dYdX Trading, and Ripple Labs in addition to his investment experience at BlackRock.
In July 2024, the Eclipse developer mainnet will be released to the public.
In September 2024, Eclipse announced the launch of the re-collateralized token tETH, powered by Nucleus.
In November, Eclipse announced that Ben Livshits joined the team as Chief Technology Officer. Ben holds a Ph.D. from Stanford University and has more than 20 years of research experience. He has worked at Intel, Microsoft, Brave, and Matter Labs.
In the same month, the Eclipse mainnet was launched.
This article is sourced from the internet: Overview of the SVM track: MoveVM is implemented, how far can SVM go?