Kripto Cüzdanı ve Borsa: Aralarındaki Farklar Nelerdir?
When getting into the kripto space, you will need to choose between a crypto wallet vs exchange to store and trade your assets. Factors like token pool and fees are crucial consideration points, but security should be at the top of your list because the cryptocurrency industry lost over $775 million in 2022.
So, it goes without saying that the platform you choose determines the safety of your funds. Therefore this article explores the differences between a crypto wallet vs exchange to keep your crypto assets away from online threats and unauthorized access. Let’s get started!
Temel Çıkarımlar
- A crypto exchange allows traders to buy, sell, and trade crypto. It acts as a middleman between buyers and sellers, facilitating transactions and providing liquidity for traders.
- A crypto wallet is an online or offline wallet that allows you to send, receive, and store crypto. Crypto wallets offer better security because users have complete control of their private keys and are not required to provide personal information.
- Examples of crypto wallets include Trezor Wallet, Exodus, Edge Wallet, Ledger Wallet, and Enjin Wallet. While examples of crypto exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, Bybit, Bitget, and Bitfinex.
What Is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet enables traders to securely send, receive, and store crypto for longer periods. These wallets also allow you to explore the Web3 ecosystem, DeFi platforms, and other decentralized applications. When comparing cryptocurrency wallets vs exchange, you will find that wallets provide better security as you control the private keys.
Private keys are cryptographic keys or passwords that enable you to sign crypto transactions, ensuring only you can authorize the movement of your cryptocurrency. When a transaction is initiated in cryptocurrency wallets, the software uses the private key to create a digital signature and then broadcasts it to the blockchain network.
Losing access to your private key or mnemonic phrase results in permanent loss of assets, and if someone else gains access to your private key, they can control your personal wallet and funds. In addition to the private keys, users are assigned a public address which is an easily shareable destination for receiving funds.
Different Types of Crypto Wallets
To secure your private keys, you will need either hot or cold crypto wallets; each has different methods and significant security implications. Here is a detailed breakdown of each wallet type to help you understand the differences and make the best choice:
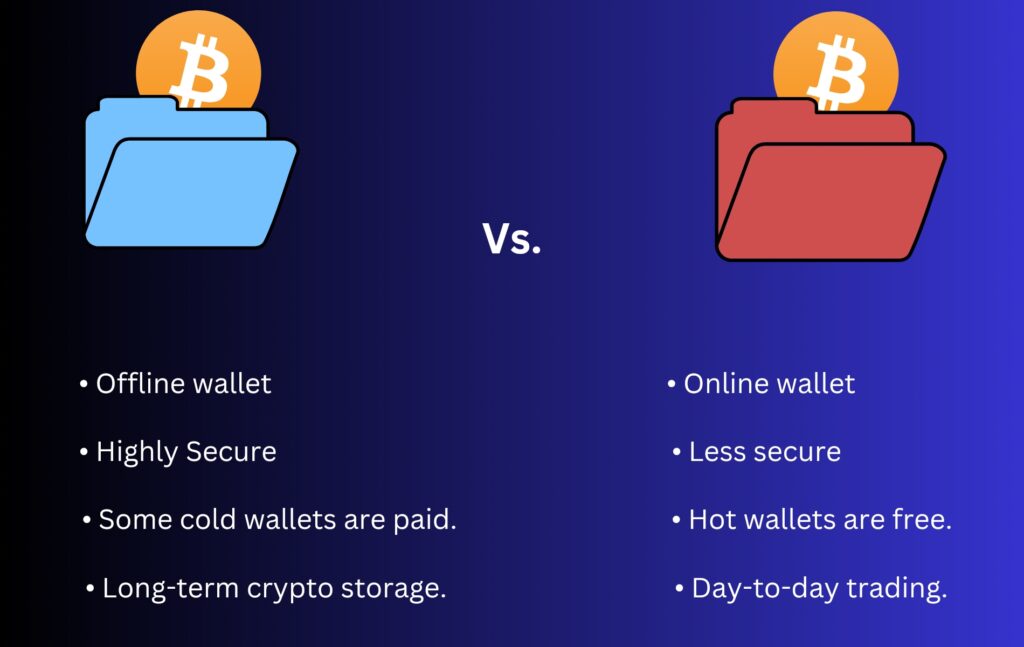
Cold Wallets
Unlike hot wallets, cold wallets are offline storage solutions, providing better security for long-term cryptocurrency holdings. Cold or hardware wallets do the opposite job of hot wallets; they sign transactions and store your private keys offline, ensuring your funds and other details are better secured from cyber attacks and theft.
While cold wallets offer better security, they are much more expensive when it comes to pricing. Using Ledger Wallet and Trezor Wallet, for instance, the first costs $79 – $149 while the latter costs $69 – 149. But before you conclude on which cold wallet you will opt for, here are the two kinds of cold wallets:
- Hardware Wallets: These physical/hardware devices store private keys offline, protecting them from online threats. They usually come in a kit with a USB cord and other products.
- Paper Wallets: Paper wallets are physical printouts of public and private keys stored securely away from digital access.
Other examples of cold wallets besides Trezor Wallet and Ledger Wallet include Opendime, CoolWallet Pro, Safepal S1, SecuX V20, Material Bitcoin, and KeepKey.
Hot Wallets (Software Wallets)
A hot wallet or software wallet is a crypto wallet connected to the internet and actively used for transactions and immediate access to funds. These non-custodial crypto wallets are designed for convenience and quick access to crypto assets, allowing users to send, receive, and store crypto without obstruction.
While hot wallets enable you to access your crypto assets quickly, it is important to balance convenience with security considerations. Due to constant internet connectivity, software wallets are more vulnerable to online threats, including hacking and malicious attacks.
That being said, here are the three types of hot wallets:
- Mobile Wallets: These are applications on smartphones for managing cryptocurrencies on the go.
- Desktop Wallets: Software wallets installed on personal computers, offering a balance of security and convenience.
- Web Wallets: Browser-based wallets allow access from any device with internet connectivity.
There are 50+ hot wallets available, and some examples include Meta maske, Electrum, Enjin Wallet, Trust Wallet, Edge Wallet, Exodus, and Bitget Wallet.
What Is a Crypto Değişme?
A crypto exchange is a platform that allows users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies for other digital assets or traditional fiat currencies like US dollars, Pounds, South African Rand, or Euros. They provide a Pazar yeri for traders and accept various payment methods such as credit cards, wire transfers, or other forms of payment.

Additionally, crypto exchanges offer features like margin trading, futures contracts, spot trading, perpetual contracts, and multiple trading pairs, with some offering up to 600 pairs. All these features are tailored to ensure a smooth experience for beginner and experienced traders.
Crypto exchanges offer public addresses and UIDs (unique identifiers) for users to receive cryptocurrency. They also require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification to verify your identity, and you must provide details like your driver’s license and government-issued ID.
Different Types of Crypto Exchanges
There are two categories of crypto exchanges—CEX (Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges) and DEX—and each exchange type offers different security measures and other features. Here is everything you need to know about these two types of exchanges.
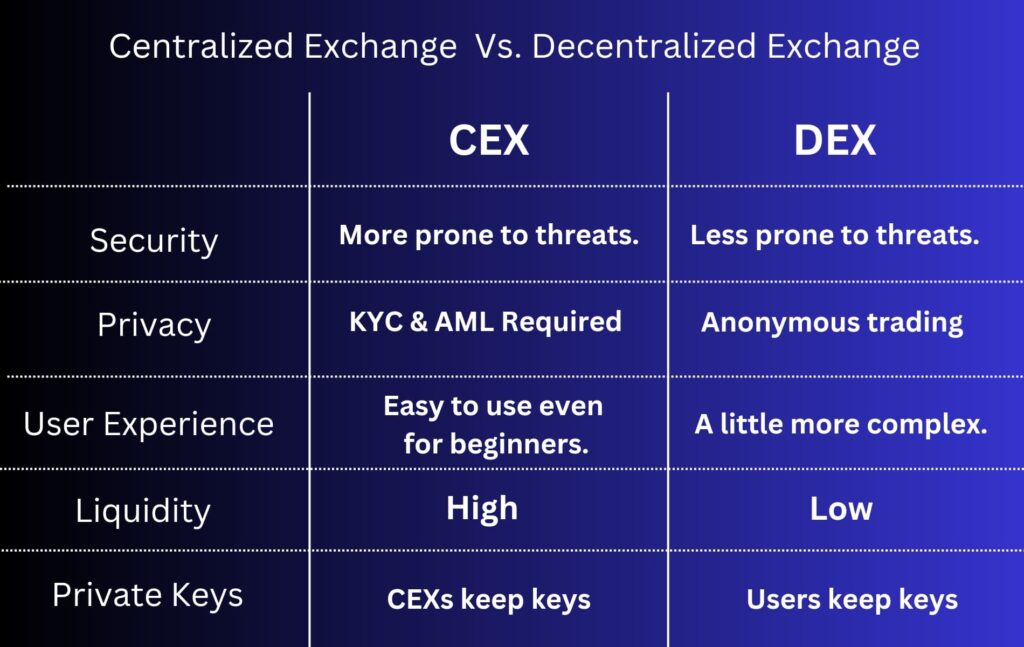
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
When you think about Centralized crypto exchanges, the first thing that should come to mind is “third party or middleman.” In Centralized exchanges (CEXs), a third party (usually the company that owns the exchange) monitors and secures the crypto transactions on your behalf.
These platforms operate as trustworthy brokers in deals and often serve as keepers, supervising and keeping your cash safe. They also enable users to carry out P2P (peer-to-peer) transactions, allowing traders to transact with other users and transfer cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies.
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) are user-friendly and offer more token options and trading pairs than decentralized exchanges. Examples of CEXs include, but are not limited to, KuCoin, Gate.io, Hotbit, Bitso Wallet, Kraken, Ve Bybit.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
A decentralized crypto exchange (DEX) is not quite different from a centralized crypto exchange. They are P2P marketplaces where users can trade digital assets directly from their wallets without a central authority. They rely on self-executing agreements written in code called smart contracts to facilitate crypto transactions.
Decentralized crypto exchanges also run on two models: The Automated market maker (AMM) or a traditional order book model.
- Automated Pazar Maker Model: Here, liquidity for an asset and its exchange pair are set in a smart contract. Traders who pool the funds are eligible to collect the fees from the swaps using this pool.
When the pool is swapped, the balance resets to a 50/50 value and the price of the tokens changes to indicate the new supply. If there is low liquidity in a pool, and a huge swap is made, the trader will run into massive slippage issues, meaning the lack of liquidity will result in an above-market purchase price.
- The Order Book Model: In the order book model, a token holder sets an order to swap his or her crypto assets for another crypto asset offered on a decentralized exchange. The holder specifies the units they want to sell the token price, and the time limit for accepting offers for the digital assets. Other users can place bids by putting a purchase order on the asset. Once the token owners decide on the time, both sides analyze and complete all offers.
Amongst the 150+ decentralized exchanges, here are examples of a few: Jupiter, Uniswap, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, Raydium, KyberSwap, Carbon, Curve Finance, and Bamboo Relay.
How is a Cryptocurrency Exchange Different From a Cryptocurrency Wallet?
Crypto Exchange and crypto wallets offer varying levels of security and different features that are unique to user needs. Below is a detailed rundown to help you better understand their benefits.
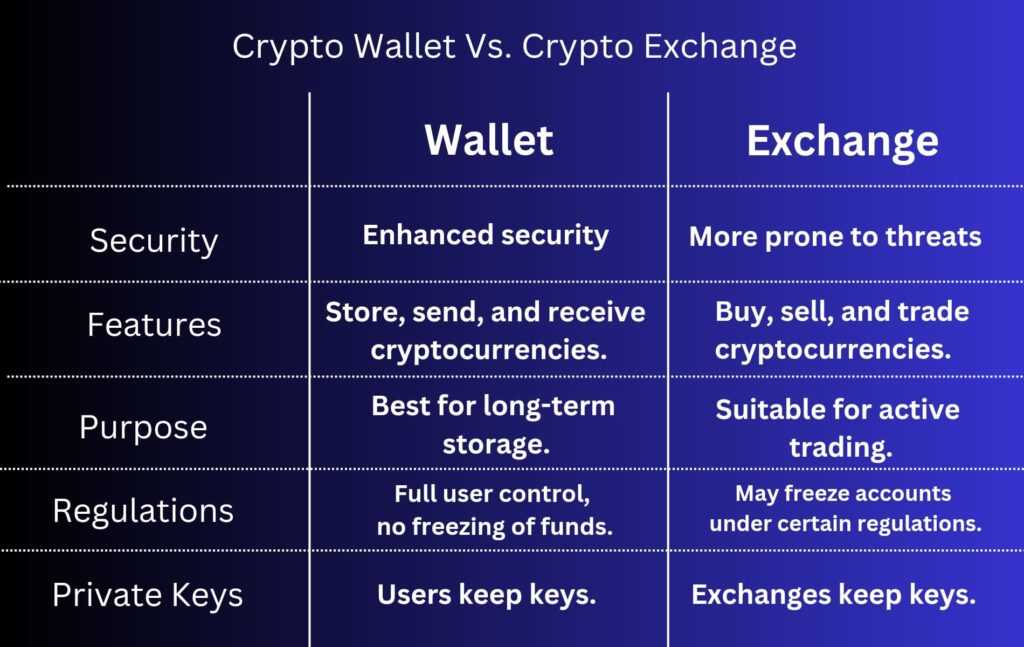
Functionality Contrast
A crypto wallet is a digital tool that stores, sends, and receives cryptocurrencies securely. Wallets do not hold the actual coins but store the private keys necessary to access and manage digital assets on the blockchain. Unlike crypto exchanges, wallets give users full control over their assets, making them ideal for long-term storage.
On the other hand, crypto exchanges facilitate the buying, selling, and trading of cryptocurrencies and the exchange of fiat currencies to cryptocurrencies or crypto to crypto. Exchanges can be centralized (CEX), where a single entity manages transactions and holds user funds, or decentralized (DEX), allowing peer-to-peer trading without a central authority.
Security Implications
One major difference between a crypto wallet and an exchange is the level of security they provide users. Crypto wallets offer traders full control over their private keys, which reduces the risk of centralized vulnerabilities. Hardware wallets, in particular, provide an extra layer of security by storing them offline.
In fact, some wallets, like Ledger Wallet and Trezor Wallet, use military-grade security chips that are impenetrable to intense physical and security breaches. On the flip side, crypto exchanges implement security measures like two-factor authentication, email verification, and cold storage to protect user funds.
Now, which one is safer? Securing private keys and recovery phrases falls entirely on you if you use crypto wallets, but centralized exchanges are active targets for scammers due to centralization. So, we recommend using both platforms for a more balanced experience.
Control Over Assets
With a crypto wallet, you have full autonomy over your private keys, personal wallet, and, therefore, crypto assets. You are solely responsible for securing your wallet and protecting your private keys. In contrast, When using a centralized crypto exchange, you entrust the exchange with your funds.
When to Use Each: Crypto Wallet Vs. Exchange
Knowing when to use a crypto exchange vs wallet is crucial, especially if you are an active trader or need a platform to store your crypto assets for long term. Here’s what we recommend: If you are storing large amounts of crypto or do not need to access your funds now and then, opt for a crypto wallet.
But if you need to trade smaller amounts of crypto or fiat currencies often, consider using a crypto exchange. Either way, combining the two platforms, one exchange and a crypto wallet will make your trading experience better and more balanced.
Son düşünceler
When you want to send, receive, or securely store crypto, a wallet is more secure than an exchange. If you opt for a wallet, you need to incorporate some form of backup system because wallets can be susceptible to failure, especially when you keep them on a flash or external drive.
On the other hand, choosing an exchange is usually a matter of convenience. But the good thing is that some exchanges, like Binance, Bybit, and Bitso Wallet, integrate a Web 3 wallet into their trading and selling functionality. This allows users to not only trade, sell, and buy crypto but also explore the Web3 ecosystem.
SSS
Is it Better to Hold Crypto in Wallet or Exchange?
If you are looking to hold crypto only, whether long-term or short-term, a crypto wallet is a better option. You will have access to high-end security measures, and you can transfer your digital assets to an exchange anytime you want to trade.
Why is a Wallet Better Than an Exchange?
While exchanges are simple, you will risk some security because your personal details and private keys are on the exchange. Besides that, some exchanges are under the 14-eyes jurisdiction, so government bodies can easily access your information at will. Also, if the exchange’s security breaches or suddenly disappears, you will lose access to your crypto without retrieving it unless the exchange comes back online.
Can an Exchange be Considered as a Wallet?
No. An exchange cannot be considered a wallet, even though some exchanges offer wallet services.
Is Binance an Exchange or Wallet?
Binance is a crypto exchange, but in November 2023, Binance launched a Web3 wallet. This wallet is a secure, self-custody wallet that allows users to explore decentralized applications.
Related: What Is USDT: A Complete Guide on Tether
Cryptocurrency excitement is reaching new heights globally. Meanwhile, many investors and market enthusiasts are curious about coins with less price fluctuation. These are known as stablecoins, which have their value linked to a specific underlying asset. The most famous and widely used stablecoin is Tether (USDT). Let’s dive into how USDT works, why it’s the top choice among cryptocurrencies, and Tether’s future perspectives. What Is Tether (USDT): USDT Meaning Tether (USDT) is a stablecoin, essentially a digital version of the US dollar. Each Tether issued is backed one-to-one by the equivalent amount in US currency held by Tether Limited in Hong Kong, meaning every USDT is meant to be worth exactly one dollar. You can exchange Tether for US dollars according to Tether company’s rules. Originally, Tether tokens were launched…







