Ancaman tersembunyi dunia blockchain: analisis lengkap serangan phishing
This article Hash (SHA 1): 418ea6548326a5f3b9496aa7912935fec8ca925c
No.: PandaLYSecurity Knowledge No.031
What is a blockchain phishing attack?
You may be familiar with the word phishing. It originally referred to those online frauds that used fake websites or emails to induce people to click on links and then defraud personal information. Now, with the popularity of blockchain and cryptocurrency, this phishing has also evolved into the blockchain world.
Blockchain phishing attacks are essentially the same as traditional phishing attacks. The attackers pretend to be someone you trust, such as a wallet website you often use, a trading platform, or even a project you have participated in. They will use fake links, fake social media accounts, or smart contracts that seem to be legitimate but actually have loopholes to lure you into entering your private key, mnemonics, or signing a malicious transaction. The result? Your crypto assets are transferred away without you noticing.
For example, imagine you see an official airdrop event on a social platform, and there is a link that looks like a wallet website you are familiar with. You click on it and enter the mnemonic, and then find that all the money in it is gone. This is a typical blockchain phishing attack scenario.
Phishing attacks are particularly cunning because they specifically target users who are not very familiar with blockchain technology and do not know enough about protection measures. Many people fall into the trap of attackers because of negligence or greed for small gains. Therefore, we must be vigilant against these attacks and guard against them at all times.
So how do you identify phishing attacks? This starts with its principle.
How phishing attacks work
There are four main types of phishing attacks, namely fake airdrops, induced signatures, backdoor tools, and providing mnemonics.
Fake tetesan udara:
The attacker uses the address generator to generate addresses that are very similar to the users wallet address (usually the first or last few digits are the same), and then transfers small amounts of funds (such as 0.001 USDT) or fake USDT deployed by the attacker to these addresses multiple times. This makes users mistakenly believe that these addresses are the normal payment addresses before. When users make new transfers, they may copy historical transaction records and mistakenly transfer funds to the attackers address, resulting in asset loss.
Induced signature:
Attackers create fake web pages, such as imitation websites of well-known projects, fake airdrop links, or shopping platforms, to trick users into connecting to their wallets and performing signing operations, thereby stealing assets.
Common induced signature attacks include the following:
-
Direct transfer
The attacker disguised the signature operation as receiving airdrops, wallet connection and other functions, but the actual operation was to transfer the users assets to the attackers address.
-
Authorized Token Transfer
The user signs a transaction on the phishing website, such as ERC 20s approve call or NFTs setApproveForAll. After obtaining authorization, the attacker can transfer the users assets at will.
-
Blank address authorization phishing
Blank address authorization phishing is an upgraded version of authorization phishing. When a user clicks on a phishing link to authorize (usually approve or increaseAllowance), the spenders address is an empty address without any on-chain record. If the victim signs the authorization, the empty address will be used to deploy a contract through the create 2 method to transfer the victims funds. Using blank address authorization can avoid the situation where the authorized address is marked by the detection tool, thereby bypassing the security check of some wallets.
-
Buy NFT Fishing for Free
Trick the user into signing an NFT sales order. NFT is held by the user. Once the user signs this order, the attacker can directly purchase the users NFT through OpenSea, but the purchase price is determined by the attacker, which means that the attacker can buy the users NFT without spending any money.
-
eth_sign blank check (blind signature)
eth_sign is also called blind signature. Using eth_sign to sign any hash value is equivalent to writing a blank check to the attacker, so the attacker can construct any custom transaction to steal user assets.
-
Permit Fishing
Permit is an extended function of the ERC 20 protocol, which allows users to complete authorization operations by signing messages and sending the signature results to another wallet, which can complete asset transfer operations. By inducing users to sign ERC 20s permit authorization, attackers can obtain the authority to transfer user tokens.
-
personal_sign signature
personal_sign is usually used to sign human-readable content, but it can also process the signed content into a hash value.
Misalnya: 0x62dc3e93b0f40fd8ee6bf3b9b1f15264040c3b1782a24a345b7cb93c9dafb7d8 message is the result of the target plaintext being hashed by keccak 256. The phished user cannot understand the content of the signature, and if he signs it, he will be phished.
Malicious multi-signature:
The original intention of multi-signature is to make the wallet more secure, allowing multiple users to jointly manage and control the use rights of the same wallet.
Taking TRON as an example, TRON multi-signature is divided into Owner (the highest authority, which can manage permissions and perform all operations), Witness (participating in voting management) and Active (used for daily operations, such as transferring or calling contracts). When a new account is created, the account address has Owner permissions by default.
When an attacker obtains a users private key through a phishing website/app, the attacker can transfer or authorize Owner/Active to his own address. Note that transfer removes the users Owner permissions, while authorization does not remove the users permissions. However, in any case, the user loses the right to transfer wallet assets.
Since users can still transfer funds, the attacker may play the long game and not transfer the victims assets immediately. The attacker will only transfer the funds after the victim discovers that his wallet has been maliciously multi-signed and stops transferring funds.
Backdoor tools:
-
Disguised as a scientists tool
Scientist tools usually refer to transaction-assisted tools used by some advanced users (so-called scientists) in the blockchain ecosystem, such as those used to quickly batch mint NFTs, batch send tokens, or quickly execute certain complex on-chain operations. Such tools are popular among primary market users because they can greatly improve operational efficiency.
However, attackers will pretend to be the developers of such tools and release seemingly legitimate tools, but actually implant backdoor programs inside the tools. These backdoor programs may secretly obtain private keys or mnemonics when users use the tools, or directly manipulate the users wallet to send tokens to the attackers specified wallet. The attacker can then control the users wallet through this sensitive information.
-
Fake browser plugins
Many users like to use browser plug-ins (such as MetaMask, Token Pocket) to facilitate blockchain transactions. Attackers may trick users into installing fake plug-ins through phishing websites. Once installed, these plug-ins will secretly record users transaction behaviors, steal private keys, and perform multi-signatures.
-
Transaction accelerators or optimization tools
Such tools usually claim to help users speed up transaction confirmation or optimize on-chain operations, and users often need to enter private keys or signatures to use these functions. Attackers induce users to enter key information during use and secretly record it.
Submit private key/mnemonic:
Attackers will create some fake trading websites or Telegram applets (such as fake Pepebot), asking users to provide private keys or mnemonics to bind their wallets, and tricking users into making “dog” transactions or other operations. In fact, attackers use these means to steal users’ private keys and then transfer all assets in their wallets.
Typical case analysis
Fake tetesan udara Scam:
When the Wormhole project released an airdrop announcement, many Twitter accounts imitated the official account and released fake airdrop links. Figure 1 The project owner is @studioFMmilano· 1 h, Figure 2 The fake project owner is @studioFMmilano, while the real project owner is @wormhole.

Induce wallet signature:
Counterfeit website signature:
Take the moonbirds-exclusive.com/ phishing website as an example. This website is a counterfeit website that imitates www.proof.xyz/moonbirds. When the user connects to the wallet and clicks Claim, a signature application box will pop up. At this time, Metamask will display a red warning, but since the signature content is not clearly displayed on the pop-up window, it is difficult for users to determine whether this is a trap. Once the user signs, the scammer can use the users private key to sign any transaction, including transferring assets.
Permit Signature:
During the staking period, a user signed a permit on a phishing website. The user checked it immediately and found no abnormal authorization. However, the phishing website later uploaded the permit offline authorization signature to the chain, which opened an authorization risk exposure for the target assets at the target address. However, the target user was not aware of this until the target user proposed the relevant re-staking ETH assets, which the phishing website immediately transferred. As a result, the user lost $2.12 million.

Figure 3. Account is signed by permit offline authorization
Malicious multi-signature:
There are many malicious multi-signature phishing methods, the most common of which are attackers deliberately leaking private keys or fake plugins/wallets
The attacker intentionally leaks the private key:
The attacker leaks the private key on social media or through other channels, and uses various tactics to trick the victim into transferring encrypted assets into the wallet. After the victim finds that the assets cannot be transferred out, the attacker transfers the wallet assets.
Fake TokenPocket wallet:
The victim searched for TP wallet on the search engine and downloaded TP wallet instead of the official website. However, the wallet actually downloaded was not the official wallet, but a fake wallet launched by the attacker on the Internet. After the user binds the mnemonic, the victims wallet will be automatically multi-signed, making it impossible to transfer assets.
Backdoor tools:
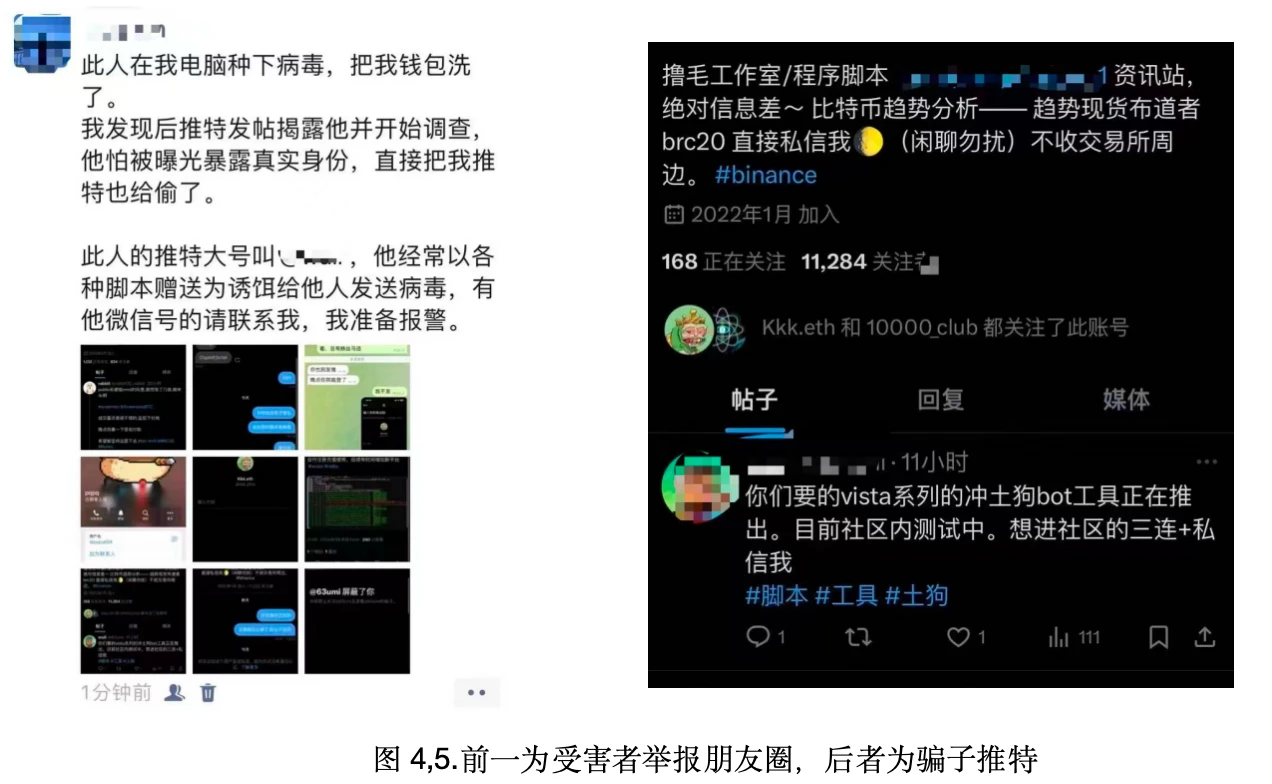
The victim found a blogger on Twitter who claimed to be a specialist in WEB-3 “massaging” and various script development. The victim downloaded and ran the script given away for free by the blogger, only to find that his wallet had been emptied and he had lost tokens worth 700 USDT.
How to Prevent Blockchain Phishing Attacks
-
Verify links and URLs
When visiting any cryptocurrency-related website, always verify the authenticity of the link and URL. Phishing attackers often create fake websites that are very similar to the official website, changing only a few characters, which can easily lead to fraud. Therefore, the first step to prevent it is to:
1. Avoid clicking on unfamiliar links: Be extra cautious when receiving any unfamiliar emails, social media messages, or links from unknown sources, especially those that claim to be promotional information, airdrop activities, or account problem prompts from official channels.
2. Use bookmarks to save frequently used official websites: When visiting cryptocurrency exchanges or wallet services, it is recommended to use the bookmarks saved in the browser directly instead of searching through search engines to avoid entering phishing websites by mistake.
-
Multi-factor authentication (2FA)
Multi-factor authentication (2FA) is one of the important measures to increase account security. When logging into an account, in addition to the password, an additional verification step is required, usually through a dynamic verification code generated by a mobile phone SMS or an authenticator application to confirm the identity.
1. Enable 2FA: Be sure to enable 2FA for all cryptocurrency accounts that support it, including exchange accounts, wallet apps, etc. Even if an attacker gets your password, they still can’t log in to your account without the 2FA verification code.
2. Use an authenticator app: Try to use an authenticator app such as Google Authenticator or Authy instead of SMS verification, as SMS may be vulnerable to SIM hijacking attacks.
3. Update 2FA devices regularly: Make sure your bound mobile phone or verification device is up to date. If your mobile phone is lost or replaced, update your 2FA device in time to avoid security risks.
-
Safety awareness training
Blockchain phishing attacks are constantly evolving, so continuous learning and security awareness are necessary.
1. Pay attention to security communities and news: Regularly pay attention to news, blogs, and community forums related to blockchain and cryptocurrency security to obtain the latest security information and warnings to avoid falling into new phishing traps.
2. Be vigilant: Develop the habit of carefully checking the operation content before any sensitive operation (such as authorization signature, transaction transfer), and do not connect to the wallet or perform signature operations on unfamiliar websites or platforms at will.
-
Wallet security management
Wallets are the core storage tools for cryptocurrencies. Proper management of wallet security plays a vital role in preventing phishing attacks.
1. Do not disclose mnemonics or private keys: Mnemonics and private keys are the key to controlling the wallet. Once leaked, attackers can directly obtain the assets in the wallet. Therefore, mnemonics and private keys must be kept properly, never disclosed to anyone, and not stored on networked devices.
2. Use cold wallets to store large amounts of assets: Cold wallets refer to wallets that are not connected to the Internet, usually hardware wallets, which are more secure. For large amounts of assets held for a long time, it is recommended to store them in cold wallets to prevent online attacks.
3. Reasonable use of hot wallets: Hot wallets are wallets connected to the Internet, which are convenient for daily transactions, but relatively less secure. It is recommended to put a small amount of daily transaction funds in hot wallets, and try to store most of the funds in cold wallets to spread the risk.
4. Back up wallet data regularly: Make sure that your wallet mnemonics, private keys, or recovery passwords are backed up reliably. It is recommended that you store the backup information in a secure, offline place, such as an encrypted USB device or physical paper.
Kesimpulan
In the world of blockchain, every step of the users operation may directly affect the security of assets. With the development of technology, phishing attack methods are also constantly upgrading, so we must always remain highly vigilant, enhance self-protection awareness, and avoid falling into scams. Whether it is verifying links, using security devices, turning on multi-factor authentication, or properly managing wallets, these small measures can build a solid line of defense for our assets.
Be extremely careful and dont act too hastily!
Lianyuan Technology adalah perusahaan yang berfokus pada keamanan blockchain. Pekerjaan inti kami meliputi penelitian keamanan blockchain, analisis data on-chain, dan penyelamatan kerentanan aset dan kontrak. Kami telah berhasil memulihkan banyak aset digital yang dicuri untuk perorangan dan lembaga. Pada saat yang sama, kami berkomitmen untuk menyediakan laporan analisis keamanan proyek, keterlacakan on-chain, dan layanan konsultasi/dukungan teknis untuk organisasi industri.
Terima kasih telah membaca. Kami akan terus fokus pada dan berbagi konten keamanan blockchain.
This article is sourced from the internet: The hidden threat of the blockchain world: a complete analysis of phishing attacks
Related: With annual revenue in the red, can Ethena survive the huge market correction?
After a weekend, Bitcoin fell below $60,000 yesterday and continued to fall today to hit $49,000, a 24-hour drop of 18.5%. Ethereum plummeted 25% to below $2,100, and the crypto market fell across the board. The market crash has made the already sluggish crypto market even worse, and the already sluggish DeFi sector has been hit hard. According to DeFiLlama data, Ethena Labs revenue has been negative in the past month. If the annual revenue is calculated based on this (revenue in the past 30 days x 12), Ethena Labs annual revenue is about negative $32.95 million. The algorithmic stablecoin USDe launched by Ethena Labs currently relies on collateral BTC, stETH and its inherent income, while creating short positions in Bitcoin and ETH to balance Delta and use perpetual/futures funding…







