Cómo liberar el potencial del mercado de billones de dólares: una mirada a las cuatro principales soluciones de expansión de Bitcoin
Autor original: TechFlow
introducción
State channels (Lightning Network), side chains (Stacks), Rollups (BitVM), UTXO + client verification (RGB++ Layer)… Who will stand out and truly unite the forces of the Bitcoin ecosystem, achieve scalability, interoperability and programmability, and introduce innovative narratives and significant increments to the Bitcoin ecosystem?
Overcapacity in infrastructure is a community voice that cannot be ignored in this cycle. When supply > demand, we can see that both new public chains and L2 are doing their best to avoid becoming ghost towns, but in the Bitcoin ecosystem, we see a completely different picture:
Since the Everyone Inscriptions craze, the market has seen the communitys enthusiasm for participating in the Bitcoin ecosystem, but due to the scalability limitations of Bitcoin, the Bitcoin ecosystem urgently needs a thorough infrastructure construction before it can truly explode. The large investments of tens of millions by institutions have prompted the Bitcoin City to roar with machines and build roads and bridges during this cycle.
For a while, it seemed that everyone wanted to get a piece of the Bitcoin ecosystems popularity, but this piece of pie is not so easy to get.
The reason is simple:
Due to characteristics such as non-Turing completeness, it is not easy to achieve Bitcoin expansion. Major projects adopt different paths, and Bitcoins expansion path is also experiencing a chaotic and exploratory period.
In this process, we can see that old Bitcoin scalability solutions such as Lightning Network, which are known for their orthodoxy, have regained new vitality, and we can also observe the wild growth of CKBs RGB++ based on RGB extension, which brings more innovative narratives. At the same time, various side chains and L2s are competing with each other, some of which are directly borrowed from Ethereum solutions, and some are improved solutions that deeply study the characteristics of Bitcoin itself.
Faced with the Bitcoin ecosystem with a trillion-dollar market potential and a wide range of technical implementation paths, which expansion protocols will stand out and truly unite the forces of the Bitcoin ecosystem, achieve scalability, interoperability and programmability, and introduce innovative narratives and significant increments to the Bitcoin ecosystem?
This article aims to explore the Bitcoin extension protocol, analyze the future trend of Bitcoin extension by comparing the advantages and disadvantages of various solutions.
1. Bitcoin expansion: the only way for Bitcoin ecosystem to explode
Following the thinking logic of first determine whether it is true, then prove why, we first discuss: Is Bitcoin expansion a false demand?
The answer is obviously no, and Bitcoin needs a scaling solution more than any other blockchain.
This argument has strong support from real situations in many aspects.
At the market level, whether it is the inscription craze or the large-scale investment of tens of millions by institutions, we can see the markets enthusiasm for the Bitcoin ecosystem. This enthusiasm is not difficult to understand. After all, in the past few years, there are still a large number of Bitcoin holders who do not just want to Hold, but suffer from the lack of more ecological participation options. When some interesting narratives are born in the Bitcoin ecosystem, coin holders are naturally eager to try.
As for Bitcoin itself, as the founder of the encryption industry, Bitcoin has gone through more than a decade of development. The interests of all participants in the ecosystem are not only intertwined but also closely linked. How to achieve a balance and maintain long-term attractiveness is also a major issue. With the fourth halving to be completed in 2024 as an example, the reduction in block rewards will lead to lower profitability for miners, which will further promote Bitcoin to explore ecological prosperity and achieve richer value flow. Bitcoin also needs an ecological environment to empower all participants in the network and further introduce incremental users.
More importantly, for the development of ecology, Bitcoin has multiple advantages that no other public chain can match: Bitcoin is driven by the community and has undergone more than a decade of stable operation. Today, its market value has reached 1.2 trillion US dollars. It has the highest popularity and recognition among the global public and investors. This gives Bitcoin an unparalleled degree of decentralization and a strong security foundation. What is more worth mentioning is that in the past, due to the lack of ecology, a large amount of Bitcoin funds were dormant and lacked a deeper degree of fund value release. This undoubtedly makes more people full of confidence in the outbreak of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Unfortunately, the performance limitations of Bitcoins underlying design have seriously hindered the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem: as we all know, Bitcoin can only process about 3-7 transactions per second, and the network will be congested during peak trading periods. In order to prioritize their transactions, users need to pay higher fees, resulting in a series of undesirable experiences such as slow transaction speeds, high fees, and long confirmation times. More importantly, Bitcoins non-Turing completeness makes it incapable of executing complex logic, which has largely discouraged many developers from building complex smart contract functions based on Bitcoin.
Faced with such a Bitcoin that is strong and expected by the market but lacks inherent conditions, expansion has become the only way for the Bitcoin ecosystem to explode. At a time when people talk less about technology and more about demand, the Bitcoin expansion protocol has gradually developed its own change and unchange construction principles by combining Bitcoins own advantages and disadvantages and using demand to reverse the solution.
The Bitcoin Extension Protocol aims to bring about a series of changes around Bitcoin’s inherent limitations:
One of the core goals of the Bitcoin extension protocol is to enhance the users transaction experience, including improving efficiency and reducing costs.
In addition, the Bitcoin Extension Protocol will also be committed to helping Bitcoin realize Turing-complete smart contract functions, allowing developers to build complex logic applications in the Bitcoin ecosystem. The realization of this function will enable Bitcoin to not only be limited to simple value transfer, but also support more diversified financial products and services, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, automated contract execution, etc. This will greatly enrich Bitcoins application scenarios and attract more developers and users.
Another important change that the Bitcoin Extension Protocol aims to bring is to enhance the interoperability between Bitcoin and other blockchains and ecosystems. By breaking the existing isolation and achieving aggregation and collaboration between different blockchains, users can more easily transfer assets and data between different platforms. This interoperability will enhance the connection of the entire blockchain ecosystem, promote resource sharing and collaboration, and promote innovation and development.
As for the advantages of Bitcoin, the Bitcoin protocol will be committed to inheriting and carrying forward:
The Bitcoin extension protocol will seek to inherit Bitcoins decentralization and strong security to a greater extent. On the one hand, this will make security more guaranteed. On the other hand, it will truly bring innovation to the Bitcoin ecosystem, rather than simply serving as a bridge to introduce Bitcoin assets into other ecosystems and prosper other ecosystems.
Another thing worth noting is that the Bitcoin expansion protocol should be expanded without changing the main network as much as possible. We know that the Bitcoin ecosystem has tried on-chain expansion solutions and upgraded them many times in the past, such as expanding block space and Segregated Witness (Segwit). This has laid a solid foundation for the subsequent Bitcoin expansion. However, since most on-chain expansion solutions will change the main network code and will sacrifice decentralization and security to a certain extent, on-chain expansion solutions are very cautious. The community has begun to prefer building off-chain solutions based on Bitcoin L1, which will not affect the underlying Bitcoin and solve performance problems.
After understanding the changes and unchanges of the Bitcoin extension protocol, we have also established some specific evaluation dimensions for how to measure the Bitcoin extension protocol. Based on these dimensions, comparing the mainstream Bitcoin extension protocols currently on the market may help readers establish a clearer understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of various technical implementation paths.
2. Introduction to Bitcoin’s mainstream expansion solutions and comparison of their advantages and disadvantages
Following different technical implementation paths, the mainstream Bitcoin expansion solutions in the market can be roughly divided into the following types:
-
State Channels
-
Sidechain
-
Enrollar
-
UTXO+ Client Verification
2.1 Canal estatal
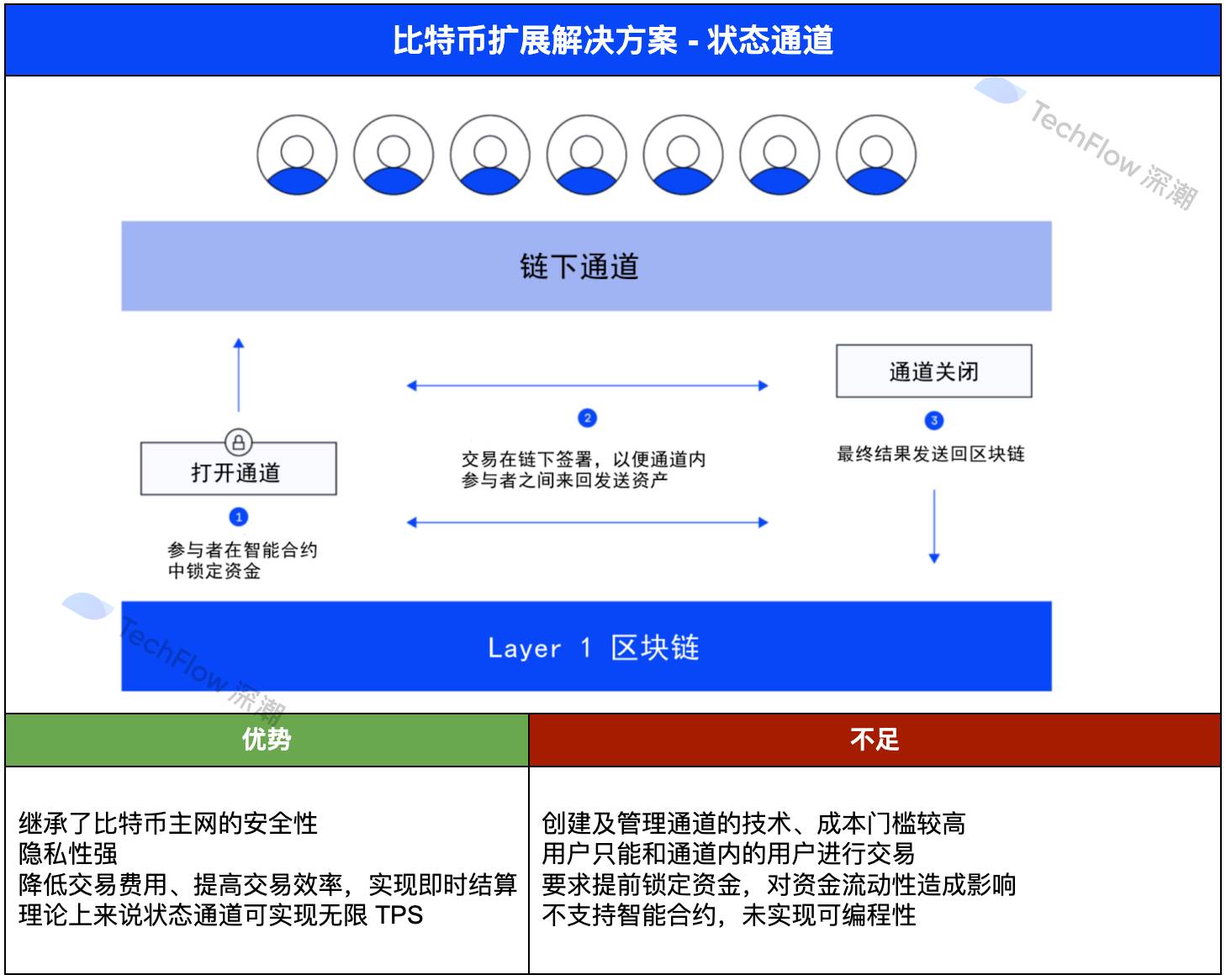
The state channel can be regarded as one of the earliest and most orthodox solutions for Bitcoin expansion attempts, and its most famous representative project is the Lightning Network.
According to its definition: a channel is established between two or more parties, and then multiple transactions are carried out within the channel, and only the final state is recorded on the Bitcoin main chain, thereby increasing speed and reducing costs.
We can explain how the state channel works through a very vivid example:
A group of people submitted a deposit to establish a WeChat payment group. Transactions in this group are not only low-cost but also fast. Finally, when the group is disbanded, the status of all payments in the group will be updated to the Bitcoin mainnet after confirmation.
Once you understand the operating logic of the state channel, you will find that the advantages and disadvantages of the state channel are very obvious:
The advantages are: on the one hand, the state channel greatly reduces the amount of computing on the main network, thereby reducing transaction costs and improving transaction efficiency; on the other hand, the Bitcoin main network verifies the final state, so the state channel inherits the security of the Bitcoin main network very well; in addition, since multiple transactions can be performed within the channel, the state channel can theoretically achieve unlimited TPS.
The shortcomings are: on the one hand, when creating a channel, both the technical and cost thresholds are high; on the other hand, users can only trade with users within the channel, which brings many restrictions; in addition, the state channel requires funds to be locked in advance, which will affect the liquidity of funds; more importantly, the state channel does not support smart contracts, which is obviously not in line with the needs of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Image source network
2.2 Sidechain
In fact, the concept of sidechain has been around for a long time. The solution is essentially an independent chain that runs in parallel with the main chain and supports users to transfer assets from the main chain to the sidechain for interaction. The main chain and the sidechain are connected through a two-way peg mechanism.
There are also many projects that adopt this technology implementation path, including not only the well-known old project Stacks, but also the rapidly rising newcomer Fractal Bitcoin that has attracted the attention of the community.
Since the sidechain is independent of the Bitcoin mainnet, in theory, the sidechain can break through the limitations of Bitcoin’s own technical framework and select the most advanced design to achieve higher performance and a better experience.
However, precisely because the sidechain is independent of the Bitcoin mainnet, the sidechain cannot inherit the strong security foundation of Bitcoin very well. Its trust foundation is built by its own consensus mechanism, and there are major centralization problems in the early stages of operation. Of course, there are currently many sidechain projects proposing innovative solutions around this issue, and working hard in their respective consensus mechanisms to better bind to the Bitcoin security foundation.
Image source network
2.3 Rollup
I believe that many people’s understanding of Rollup comes more from Ethereum L2. In the fiercely competitive Ethereum L2 track, projects that adopt Rollup solutions occupy half of the market. In this round of Bitcoin infrastructure boom, the Rollup technology path also shines in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Projects such as B² Network and Bitlayer have developed into popular projects in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In terms of specific operating logic, Rollup executes transactions off-chain, aggregates multiple transactions into batches, and then publishes these batches to the main chain at one time. This mechanism places data availability on the main chain to inherit the security and decentralization of the main chain, and significantly reduces the amount of data that must be stored on the chain, which may alleviate congestion on the Bitcoin network and reduce transaction costs.
But unlike Ethereum Rollup, Ethereum has a virtual machine, which means that most Ethereum Rollups use the Ethereum blockchain as the data availability layer and consensus layer, but Bitcoin does not have a virtual machine. How does Bitcoin L1 verify the validity of the Rollup proof? This poses more challenges to Bitcoin expansion projects that choose the Rollup technology solution.
There are currently three different types of Rollups in the Bitcoin ecosystem, but none of the three models are perfect:
OP Rollups is based on the principle of trust, and transactions are considered valid by default, but there is a challenge period. This model is simpler, easier to integrate, and allows for greater scalability, but due to the existence of the dispute window, there will be delays in the final confirmation of transactions.
Sovereign Rollups take a more independent approach, placing data availability on the main chain, but performing transaction verification and execution through their own consensus mechanism. This model allows Rollups to share the Bitcoin security foundation while being unrestricted by Bitcoin scripts, but places high demands on the consensus mechanism of the Rollups themselves.
Validity Rollups (including ZK Rollups) use cryptographic proofs to verify the correctness of off-chain transaction batches without leaking the underlying data. This approach combines efficiency and security, but the complexity and computational requirements of generating ZK proofs have always been a challenge.
Image source network
2.4 UTXO + Client Verification
If Rollup is like an imported product of Ethereum in the eyes of most people, then UTXO + client verification is more like a customized solution designed based on the characteristics of Bitcoin itself.
If you want to introduce UTXO + client verification intuitively, you will have to spend more time and effort. On the one hand, it is due to its own technical complexity, and on the other hand, it is due to the many optimizations and evolutions of the solution in the past few years.
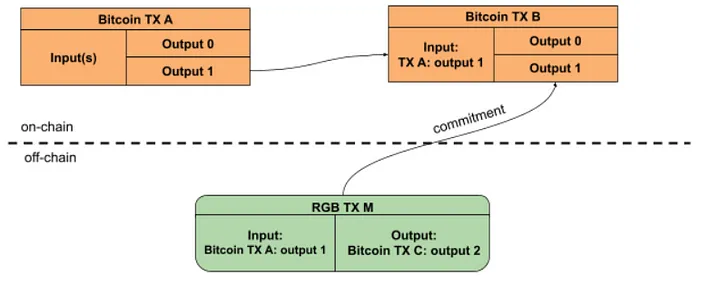
We know that Bitcoin does not have the concept of accounts, but adopts the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model, which is the core concept of Bitcoin transactions and the design basis of the UTXO + client verification technology path. Specifically, the solution attempts to perform off-chain ledger calculations based on Bitcoin UTXO and ensure the authenticity of the ledger through client verification.
The idea originated from the concepts of single-use seal and client-side validation proposed by Peter Todd in 2016, and eventually led to the birth of the RGB protocol.
As the names suggest, one-time seal is like an electronic seal that ensures a message can only be used once, while client-side verification aims to move the verification of token transfers from Bitcoin’s consensus layer to off-chain, where it is verified by the client associated with a specific transaction.
The core idea of RGB is that users need to run the client themselves and verify the asset changes related to themselves. In simple terms, the asset recipient needs to first confirm that the asset senders transfer statement is correct before the transfer statement can take effect. This series of processes takes place off the Bitcoin chain. That is, complex smart contract calculations are placed off the chain to achieve efficiency and privacy protection.
So how to inherit the strong security of Bitcoin? RGB uses Bitcoin UTXO as a seal, and corresponds the RGB status change to the ownership of Bitcoin UTXO. As long as Bitcoin UTXO is not double-spent, the bound RGB assets will not be double-spent, thus inheriting the strong security of Bitcoin.
Admittedly, the birth of RGB is of great significance to the Bitcoin ecosystem, but things are always rough in the initial stages of development, and RGB still has many defects:
For example, when ordinary users use simple client products, they do not have the ability or resources to save all historical transactions, and therefore it is difficult to provide transaction proof to the counterparty. Different clients (users) only store data related to themselves and cannot see the asset status of others, which can easily lead to client data island problems. This method, which is neither globally visible nor data transparent, has also seriously hindered the development of applications such as DeFi.
For another example, RGB transactions, as an extension of Bitcoin transactions, rely on a P2P network for transmission. Users also need to interact when transferring money, which all rely on a P2P network independent of the Bitcoin network.
More importantly, the virtual machine of the RGB protocol mainly uses AluVM, which lacks perfect development tools and practice codes, and the RGB protocol currently does not have a perfect interaction solution for ownerless contracts (public contracts). This makes multi-party interaction difficult to achieve.
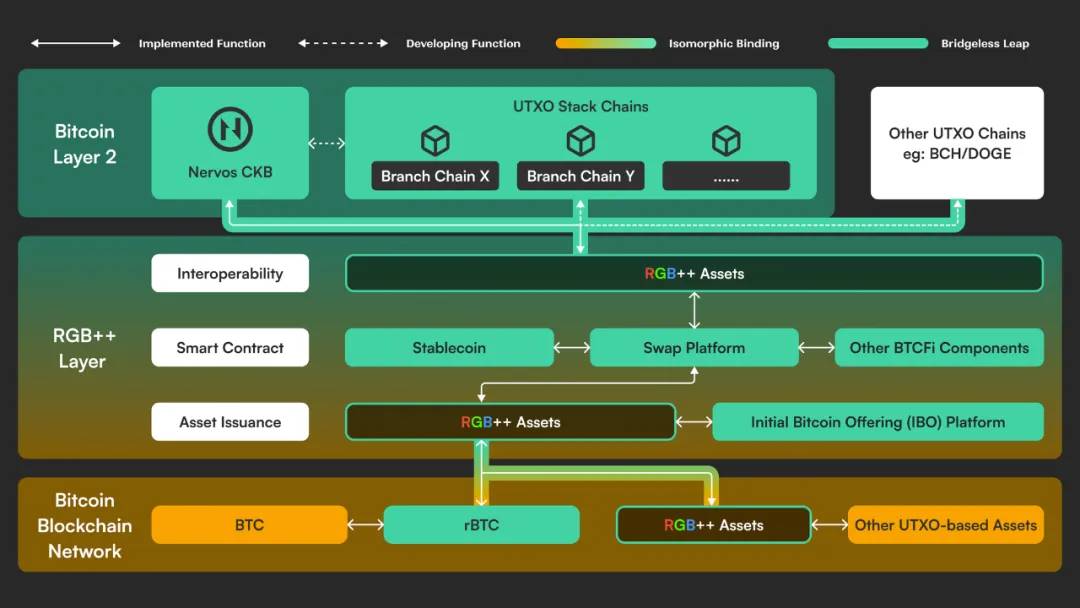
It is precisely because of the existence of these problems that Nervos Network, a long-established public chain project known for its technology, began to explore more optimized solutions, and RGB++ came into being.
Although RGB and RGB++ are closely related in name and both originate from important concepts such as one-time sealing and client verification, RGB++ is not an extension of RGB. In fact, RGB++ does not use any RGB code. More strictly speaking, RGB++ is a complete reconstruction based on the RGB concept to achieve a series of optimizations.
The core idea of RGB++ is to hand over the data verification work originally done by users to make it globally verifiable. Of course, users can also run their own clients to verify RGB++ data and related transactions.
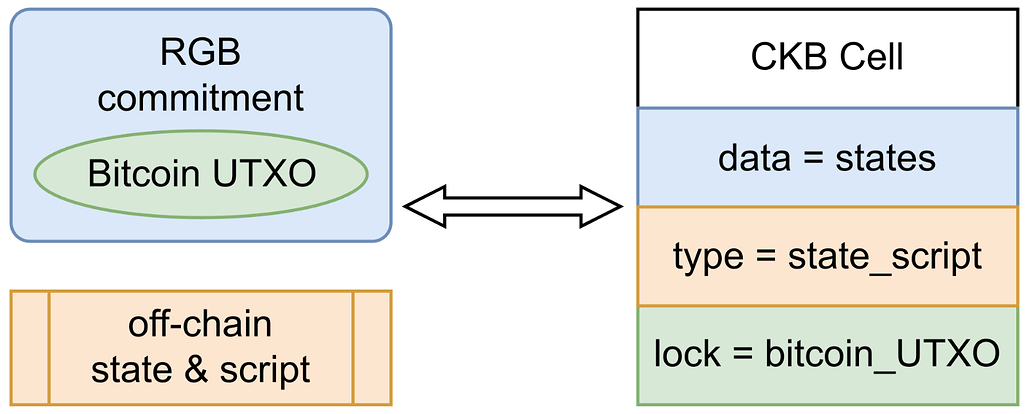
Who will it be handed over to? Public chains and platforms that support UXTO and expand the programmability given by UXTO, such as CKB, Cardano, etc.
How to transfer? This involves the important concept of isomorphic binding: Bitcoin is the main chain, CKB and Cardano are like shadow chains of the Bitcoin main chain, and the extended UTXO on CKB, Cardano and other chains is used as a container for RGB asset data. The parameters of RGB assets are written into these containers to achieve the binding of the main chain and the shadow chain, and the data is directly displayed on the blockchain.
Taking CKB as an example, due to the properties of Cells extended version of UTXO, Cell can establish a mapping relationship with Bitcoin UTXO, allowing CKB to serve as a public database and off-chain pre-settlement layer for RGB assets, replacing the RGB client and achieving more reliable data custody and RGB contract interaction.
In this way, on the one hand, RGB++ inherits the strong security foundation of Bitcoin. On the other hand, the functions brought by RGB++, such as non-interactive RGB transactions, commitment release of aggregated multiple transactions, and BTC assets interacting directly with CKB on-chain assets without cross-chain, will further unlock more use cases such as DeFi.
Due to its outstanding advantages in security, efficiency and programmability, RGB++ has been well received by the industry since its launch, although it has a high cognitive threshold. It has become one of the Bitcoin extension protocols with mainstream supporters. With the completion of the upgrade of RGB++ to RGB++ Layer in July 2024, Bitcoin extension has once again ushered in a moment of innovation.
From the name of this upgrade, we can capture a lot of information: from protocol to layer, RGB++ is bound to develop towards a wider range of services, deeper aggregation and more seamless interaction.
Just like each country (blockchain) has its own operating rules at the beginning, the RGB++ Layer aims to find a common point (UXTO) and use this common point to connect the important elements of ecological development, achieve a higher degree of same writing, same track, and build a more powerful expansion infrastructure layer for the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
First of all, as an infrastructure, RGB++ Layer must be easy to understand and widely accepted: RGB++ Layer has a complete native AA solution and is well compatible with the account standards of other public chains. This feature not only facilitates support for some key scenarios, but also clears obstacles for UX.
RGB++ Layer is more committed to achieving the unification of asset issuance: RGB++ Layer supports the issuance of various RGB++ assets, including user-defined tokens (UDT) similar to ERC 20 and digital objects (DOB) similar to ERC 721. Thanks to the advantages of the UTXO model, RGB++ Layer can create a new paradigm for asset issuance, supporting the issuance of the same asset on multiple chains at the same time, with different proportions on each chain. This not only achieves coordination and unification between different chains, but also provides asset issuers with a high degree of flexibility.
Now that asset issuance can be unified, asset interaction will be more seamless: through the RGB++ Layer bridgeless cross-chain (Leap), assets on the UTXO chain can cross to another UTXO chain without a cross-chain bridge. This not only brings stronger security, but also achieves higher interoperability. Various assets based on UTXO chains such as Cardano, Dogecoin, BSV and BCH can be seamlessly integrated into the Bitcoin ecosystem.
After breaking through the two major barriers of asset issuance and asset interaction, RGB++ Layer aims to bring a unified smart contract framework and execution environment to the Bitcoin ecosystem through CKB-VM, giving Bitcoin more powerful programmable properties: any programming language that can support RISC-V virtual machines can be used for contract development on RGB++ Layer to build complex logic applications, making the outbreak of BTCFi and the implementation of more innovative scenarios possible.
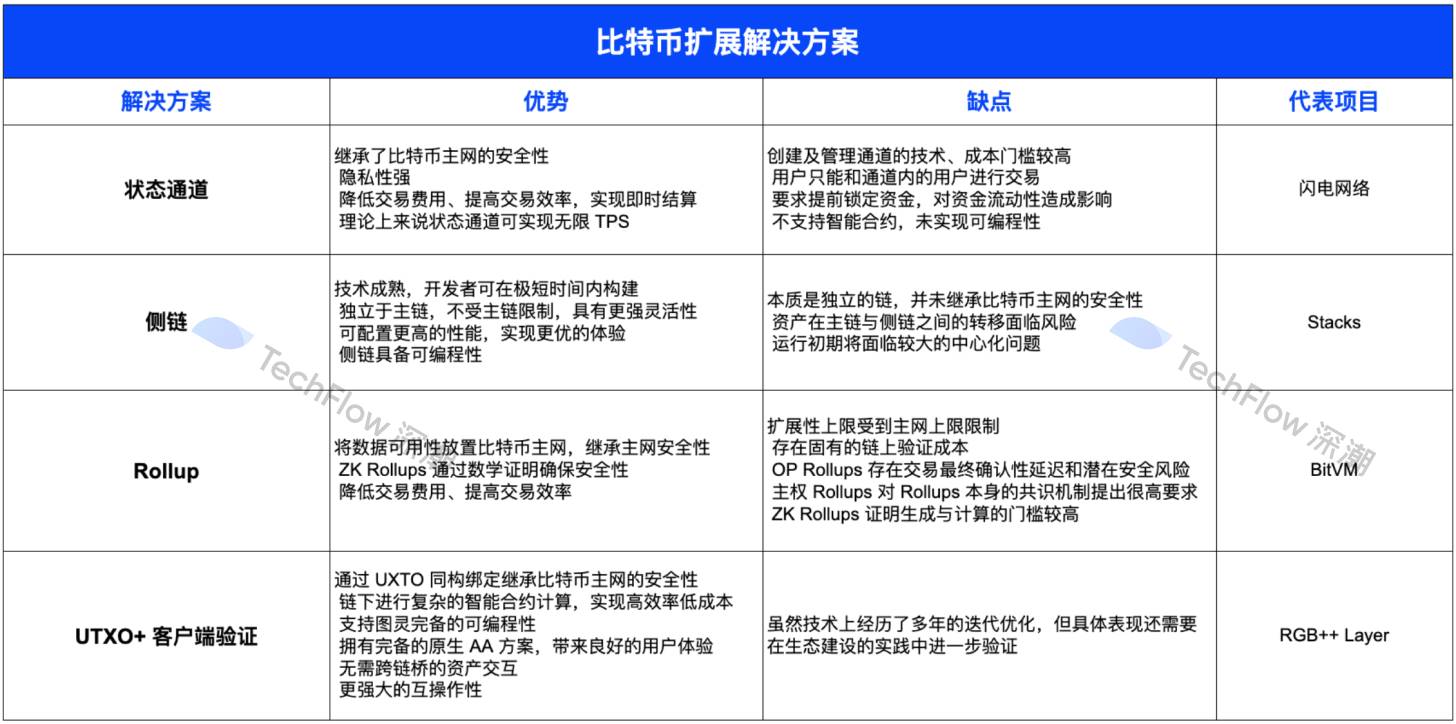
At this point, this article has introduced the basic operating logic, representative projects, and advantages and disadvantages of the four mainstream Bitcoin extension protocols. Readers can review the content through the chart below and understand the advantages and disadvantages of various Bitcoin extension protocols more intuitively and clearly.
Of course, the above content is all sorted out and summarized from the past performance of major solutions. Faced with the Bitcoin ecosystem that is ready to take off in this cycle, the representative projects in the ecosystem of major technology implementation paths are not indifferent, but are constantly seeking innovation and breakthroughs to seize a better ecological position.
Therefore, after comparing with the past, we should focus on the future, and take a look at the future competitive landscape of Bitcoin expansion solutions by understanding the change-seeking rules of the leading solutions projects.
3. The current status and future potential of the ecosystem of the major schemes and protocols
3.1 Lightning Network: A synonym for “legitimacy” and a move towards a multi-asset network
The legitimacy of the Lightning Network can be traced back to 2009, when Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto included a draft code for the payment channel in Bitcoin 1.0, which was the prototype of the Lightning Network.
After more than a decade of development, the Lightning Network has become very mature. According to 1ML statistics, the Lightning Network currently has 12,700 nodes, 48,300 payment channels, and about 5,212 bitcoins in channel funds, and has established cooperation with multiple social and payment projects.
Comparing the data of 13,600 nodes, 51,700 channels and 4,856 bitcoin funds in May this year, we can find that not only the growth rate of funds in the Lightning Network has slowed down, but the number of channels has even declined. Looking at the community opinion, we have also heard some negative comments in recent years.
On the one hand, in the early stages of the development of the Lightning Network, many developers have already realized the many limitations and challenges of the technology in terms of scalability, and the Lightning Network protocol is too complex, and the development process is slow, difficult and time-consuming;
On the other hand, after several years of development, most peoples understanding of it is limited to payment. Anton Kumaigorodski, a core developer of the Lightning Network, once said on social media: In addition to payment, people should look for other directions. This further pushed the Lightning Network to a crossroads of transformation.
What is even more regrettable is that it seems that team disagreements have always accompanied the development of the Lightning Network. Over the past year or so, many developers have left one after another, which has made the already difficult development process even worse.
Of course, faced with difficulties, the Lightning Network did not sit idly by. In addition to continuing to develop its advantages and deepening its presence in the micropayment track, with years of experience in the payment field, the Lightning Network gradually realized that compared to Bitcoin assets, the Bitcoin currency network narrative is more attractive, and began to move towards building a multi-asset network.
On July 23, 2024, Lightning Labs released the first mainnet version of the multi-asset Lightning Network, officially introducing Taproot Assets to the Lightning Network.
Before the emergence of the Taproot Assets protocol, the Lightning Network only supported Bitcoin as a payment currency, and its application scenarios were very limited.
With the launch of the multi-asset Lightning Network mainnet version, anyone or organization can use the Taproot Assets protocol to issue their own tokens. It also supports the issuance of stablecoins corresponding to fiat currencies, and the assets of the Taproot Assets protocol are fully compatible with the Lightning Network, making it possible for Lightning Network to achieve global instant settlement of foreign exchange transactions, pay for stablecoins to purchase goods and other application scenarios. This will further promote the Lightning Network to become the infrastructure of the global payment network.
3.2 Stacks: An established sidechain project, Nakamoto upgrade completed
In the Bitcoin ecosystem, Stacks is very unique. It is not only an OG project launched in 2017, but also obtained approval from the U.S. Securities and Intercambio Commission (SEC) under Regulation A+ in 2019, becoming the first token sale approved by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
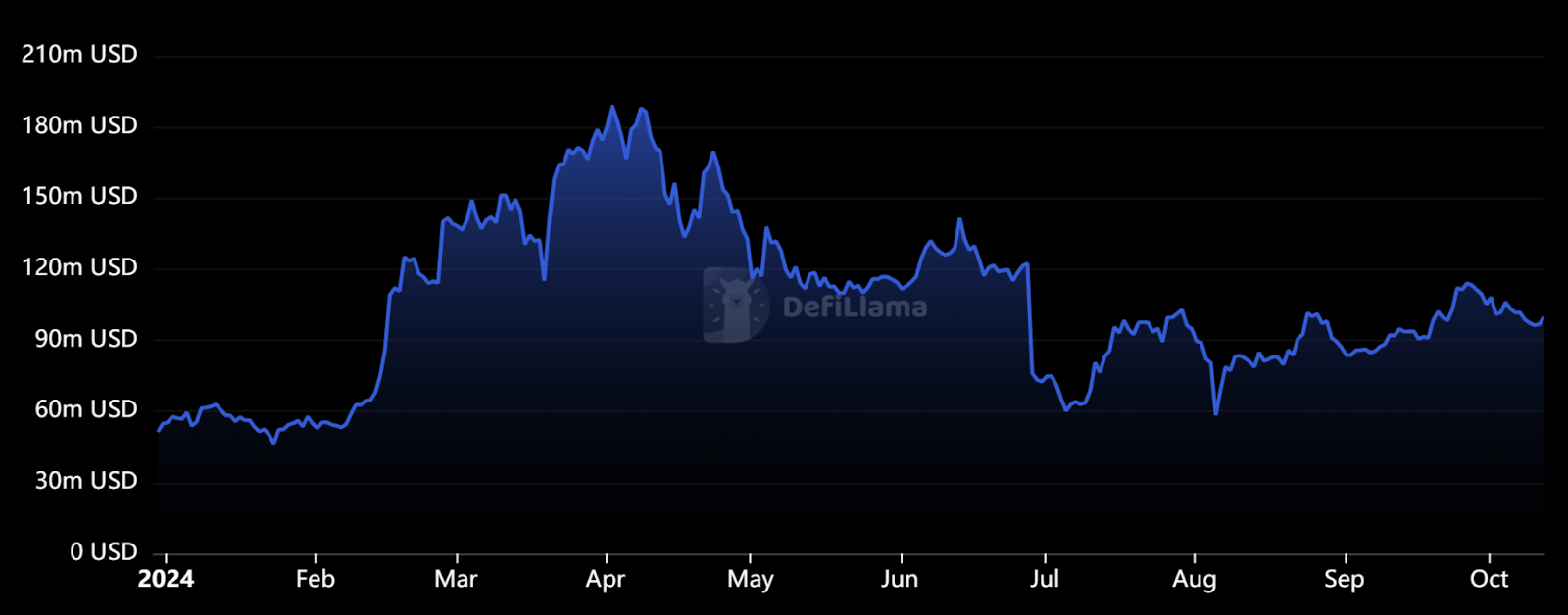
According to DeFi Llama data, with the popularity of inscriptions, Stacks TVL has continued to grow since the beginning of 2024, reaching $183 million in early April, but with the decline of inscriptions, Stacks TVL has fallen back and is currently around $100 million. But it is worth mentioning that after several years of development, the active DeFi on the Stacks chain is remarkable. For example, StackingDao, the liquidity staking project ranked first in TVL, has more than 30,000 real staking users, and the cumulative number of independent wallets of Stacks has exceeded 1.21 million.
However, as a sidechain project, Stacks also faces many challenges in its development:
On the one hand, the security of the chain is highly dependent on the budget of Stacks miners. The connection structure between the Stacks chain and the Bitcoin network (such as the transfer proof mechanism) helps to improve decentralization and security, but limits the on-chain performance and scalability.
On the other hand, although the side chain has higher flexibility, since it is essentially a new chain built outside the Bitcoin chain with an independent governance structure and transaction model, some people also believe that Stacks is not orthodox and has little recognition in the Bitcoin community.
Recently, the most milestone moment in the Stacks ecosystem is the Stacks Nakamoto upgrade: this upgrade will not only bring stronger security to Stacks, but also greatly improve the block confirmation time, achieving a transaction speed of about 5-10 seconds, which is about 100 times faster than the current transaction speed.
At the same time, the Stacks core team is also developing sBTC as a trustless solution to bridge BTC from the Bitcoin main layer to another chain. sBTC builds a bridge between the Bitcoin network and the Stacks chain for BTC assets. Its permissionless and open participation features will further unleash DeFi innovation for Stacks and bring a $10 billion TVL opportunity.
3.3 BitVM: Introducing expression logic directly into Bitcoin
As mentioned above, Bitcoin has no virtual machine, so it is difficult to verify the validity of Rollup proofs. The birth of BitVM is dedicated to introducing expression logic directly into Bitcoin without making any changes to Bitcoin itself, helping to realize off-chain computing and verify any calculation on the Bitcoin blockchain. This development not only emphasizes security and efficiency, but also opens the door to Bitcoin programmability (such as Turing-complete smart contracts).
Although BitVM is in its early stages, it has also attracted attention from projects and the community. Currently, many projects including Bitlayer, Citrea, Yona, Bob, etc. use BitVM.
Currently, BitVM itself is still improving its mechanism. The upcoming major upgrade of BitVM 2 and BitVM Bridge are one of the manifestations:
BitVM 2 aims to perform complex calculations off-chain and conduct fraud proofs on-chain. This design cleverly implements Turing-complete computational verification based on Bitcoin’s limited scripting capabilities.
BitVM Bridge adopts a new 1-of-n security model, in which theft can be prevented as long as there is one honest participant. It is regarded as a catalyst for greatly improving the security and decentralization of Bitcoin cross-chain and promoting the development of BTCFi.
It is worth noting that although BitVM 2 greatly simplifies the verification process, the Gas cost of on-chain verification is still not low. In addition, BitVM is essentially a virtual computer concept that has not been implemented, and its operating logic has not completely broken through the limitations of ZK Rollup and Optimistic Rollup. For this reason, many members are taking a wait-and-see attitude towards BitVM.
3.4 RGB++ Layer: Bitcoin asset issuance layer, smart contract layer and UTXO interoperability layer
After completing the RGB++ Layer upgrade, RGB++ Layer shifted its focus from the brand narrative level to a more refined implementation path, and chose BTCFi as the construction focus to carry out a series of technical iterations and ecosystem construction. It then announced that it would launch a series of important updates and innovative products, dedicated to integrating the Bitcoin asset issuance layer, smart contract layer and interoperability layer into one, and moving rapidly towards a safer, more seamless and more efficient Bitcoin infrastructure layer.
At the asset issuance level, RGB++ Layer is introducing a new asset issuance model called IBO (Initial Bitcoin Offering). Its core feature is that it supports the creation of a funding pool directly on UTXOSwap, allowing newly issued assets to be traded with high liquidity, which not only takes into account fairness but also mobilizes community enthusiasm, bringing a new paradigm of asset issuance to RGB++ assets and even the Bitcoin ecosystem.
As a decentralized exchange built on RGB++ Layer, UTXOSwap adopts intent-based transactions as its core, implements the process of off-chain matching and on-chain verification, and uses the parallelism of UTXO to improve transaction efficiency. It aims to become the central hub of RGB++ Layer, bringing together the liquidity of various UTXO chains and laying a good foundation for the development of DeFi.
Stablecoins are one of the three pillars of DeFi development, and RGB++ Layer has already made arrangements in this regard: Stable++, as a decentralized over-collateralized stablecoin protocol, can leverage the powerful Turing-complete programmability of RGB++ Layer to efficiently build over-collateralized vaults and liquidation modules, supporting users to use BTC and CKB as collateral to mint the US dollar-pegged stablecoin RUSD. Thanks to the powerful interoperability of RGB++ Layer, RUSD is compatible with all UTXO chains and circulates freely within the Bitcoin ecosystem, becoming an important part of BTCFi liquidity.
In addition to being an innovator, RGB++ Layer is also committed to becoming an enabler of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Through a strong alliance, it further integrates liquidity and application scenarios to promote the further outbreak of the Bitcoin ecosystem. UTXO Stack and Fiber Network are one of the concentrated manifestations.
In September, UTXO Stack announced its transformation into the Lightning Network staking layer and launched a corresponding token incentive mechanism to encourage users to stake CKB and BTC to enhance the liquidity of the state channel. The series of initiatives aim to provide better liquidity and a better profit model for the Lightning Network, paving the way for the large-scale popularization of the Lightning Network.
Fiber Network is an L2 network based on CKB. Its initial functions are similar to those of Lightning Network. It aims to become a high-performance, low-cost micro-transaction payment network. However, compared with Lightning Network, due to the Turing completeness of CKB, Fiber Network has greater flexibility in liquidity management, and is more efficient, less expensive, and has a better user experience. More importantly, compared with Lightning Networks focus on the single currency BTC, another major new feature of Fiber Network is its support for multiple assets, including BTC, CKB, and Bitcoins native stablecoin RUSD and other RGB++ assets, which will pave the way for complex cross-chain financial applications.
However, the birth of Fiber Network is not to replace Lightning Network. The ultimate goal of Fiber Network is to become a programmable expansion solution for the Bitcoin ecosystem. In this process, Fiber Network will work closely with Lightning Network. The technology stack of Fiber Network mainly includes CKBs Cell, RGB++ Layer, Bitcoin scripts HTLC and Lightning Networks state channel. The first test version released by Fiber Network has verified the feasibility of transferring BTC assets on Lightning Network to CKB in a decentralized manner, which allows more BTC assets to circulate on CKB.
Since Fiber Network and Lightning Network are technically isomorphic, they naturally have the basis for realizing cross-chain atomic swaps. This combination of Bitcoin-level security + Ethereum-level functionality + Lightning Network-level speed will not only shine in the payment field, but also promote the Bitcoin ecosystem to realize DeFi applications such as native stablecoins, native lending, native DEX, and further promote the outbreak of BTCFi.
Conclusión
In this article, we have learned about the various Bitcoin scaling solutions:
The state channel can theoretically achieve unlimited TPS;
Sidechains have outstanding flexibility advantages;
The success of Rollup in the Ethereum ecosystem has made more people look forward to its development in the Bitcoin ecosystem;
UTXO + client verification has undergone multiple iterations and evolutions, and the RGB++ Layer is more like a culmination of various attributes. It not only inherits the security of the Bitcoin mainnet, but also has multiple advantages in user experience, programmability, and interoperability. From a technical theoretical point of view, it is a relatively mature and complete Bitcoin expansion solution.
However, it is worth noting that although RGB++ Layer has been iteratively optimized and has a clear development path, its specific performance still needs to be further verified in the practice of ecological construction. With the implementation of multiple project roadmaps and the launch of products in the ecosystem, will RGB++ Layer become a huge driving force for unleashing the potential of BTCFi?
The battle for Bitcoin expansion has not yet been determined, and various plans have shown their strengths. The community is waiting to see which one will stand out in the end.
This article is sourced from the internet: Unleashing the trillion-dollar market potential, a look at the four major Bitcoin expansion solutions
Related: Interactive Guide: A step ahead to teach you how to play with the Story Protocol ecosystem
Original author: Karen, Foresight News Content is king, IP is supreme. In this era of information explosion and rapid development of generative AI, the power of IP will be everywhere. At the end of August, the on-chain IP protocol Story Protocol launched its first public testnet Iliad, which supports users to mint IP assets on Story Network and transform IP into liquid, programmable and ownable digital assets. Recently, in an exclusive interview with Story Protocol co-founder Jason Zhao by Foresight News ( Exclusive Interview with Story Protocol Co-founder: The Trillion-Dollar IP Mercado Needs to Be Reshaped ), Jason Zhao elaborated on Story’s vision: “We are not the programmable intellectual property layer of the blockchain, we are the programmable intellectual property layer of the Internet. What is really important is not…