This article is for technical sharing only and does not constitute any investment advice.
Will BTC also have its own smart contract?
Recently, in the Bitcoin ecosystem, Fractal BTC finally launched its mainnet in September after multiple testnets. One of the major features of Fractal is its smart contract capability, and it launched a new token protocol CAT 20 almost at the same time as the mainnet was launched. What technical ingenuity does CAT 20 have? What can we learn?
Fractal Bitcoin
Before understanding CAT 20, we need to have a brief understanding of Fractal Bitcoin. Their relationship is like that between ERC 20 and ETH. The CAT 20 protocol is deployed on Fractal Bitcoin.
Fractal Bitcoin, also known as fractal Bitcoin, is a second-layer network that is fully compatible with BTC. Compared to BTC, its block confirmation time is faster, only 1 minute. Its basic principle is simply as its name suggests, that is, the BTC network is copied several times, and each chain will process transactions. With more nodes that can process transactions, the speed will naturally be faster. However, the specific details such as how different chains communicate with each other are not very clear at present, and there is no official corresponding technical documentation for reference.
If it is just a second-layer chain transaction that is faster, it seems that there is nothing exciting. However, in Fractal, the opcode OP_CAT, which was abandoned by BTC a long time ago for security reasons, is enabled, which makes Fractal Bitcoins capabilities rise to a higher level. Some people say that OP_CAT can make BTC have the ability of smart contracts, which leaves more room for imagination.
Now, someone has implemented a protocol similar to ERC 20 on Fractal Bitcoin.
We will discuss why OP_CAT was abandoned and why it can be used on Fractal Bitcoin in detail later. Here we focus on CAT 20.
CAT Protocol The following content refers to the white paper: Introduction | CAT Protocol ( https://catprotocol.org/ )
And GitHub repository: GitHub – CATProtocol/cat-token-box: A monorepo for packages implementing CAT protocol ( https://github.com/CATProtocol/cat-token-box )
With the underlying OP_CAT support, a corresponding protocol, CAT Protocol, will soon be available. Currently, a protocol that is already running is the CAT 20 protocol, and a corresponding panel has been added on Unisat: https://explorer.unisat.io/fractal-mainnet/cat20 .
Seeing the name CAT 20, you should be able to react that it should be similar to ERC 20. Compared with the mature ERC 20 protocol, it is already very convenient for everyone to deploy a token. How does CAT 20 achieve a similar life cycle to ERC 20?
Deploy
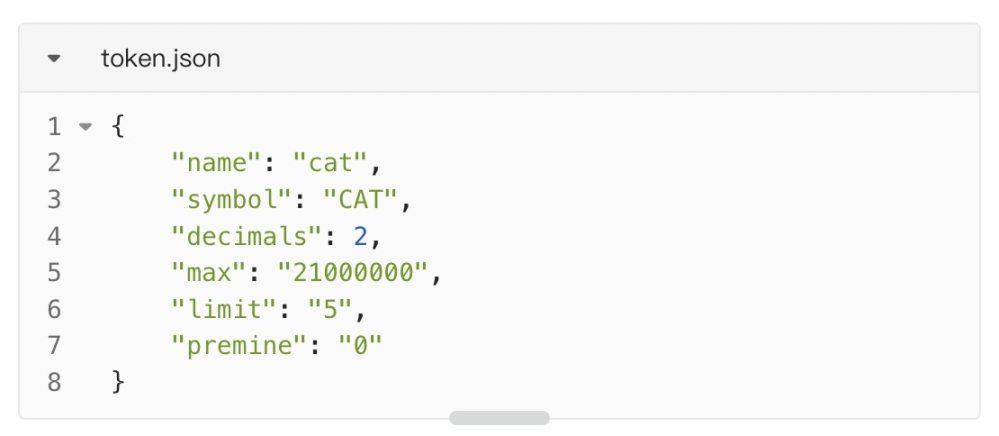
Before deployment, users need to specify their wallet address and basic information of the token. The basic information of the token is similar to that of ERC 20:
There will be some differences. CAT 20 can set the pre-mining and mint quantity limit each time. Of course, ERC 20 can also achieve these capabilities through the contract capabilities.
During the deployment phase, two transactions are initiated, which can be considered as two stages: commit and reveal. Referring to the official diagram, the deployment stages are as follows:
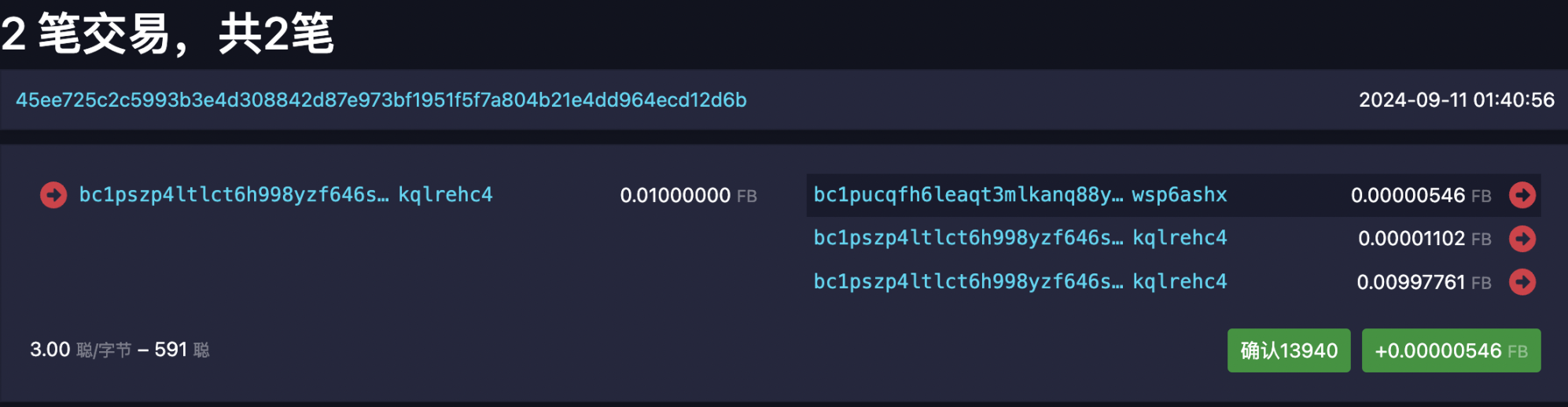
In the commit phase, the basic information of the token will be written into the output script of the transaction, such as the name and symbol of the token. The hashId of the transaction initiated in the commit phase will be used as the logo of the token to distinguish it from other tokens.
You can see that the utxo of this transaction bc 1 pucq…ashx corresponds to commit. Then the remaining two transactions point to bc 1 pszp…rehc 4. The first one is used to pay the gas fee for the following reveal stage, and the other one is for change.
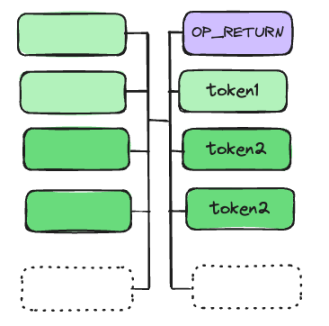
In the reveal phase, we can see that there are two utxo inputs, corresponding to the first two outputs in the previous commit phase. This transaction will first output an OP_RETURN, in which the hash of the initial state of CAT 20 will be saved. After that, a Minter will be output, which will play an important role in the subsequent Mint process and is used to maintain the state changes of the Mint process.
Looking back at the entire Deploy process, commit and reveal follow the two steps of submission and disclosure commonly used on the blockchain. It is a relatively common way to deploy projects. Some data of the project will only be revealed in the reveal stage.
Mint
Let鈥檚 first look at the Mint Simbólico transaction.
As you can see in the figure above, Mints process has the following characteristics.
-
The input of mint is a minter, which is initially generated during deploy.
-
Each mint has only one minter as input and any number of minters as output (a bit problematic)
-
Each mint has only one token (a bit problematic)
-
The output order is required, minter must be followed by token
Knowing the Mint process, we can actually find some special situations that will make the entire Mint process interesting.
For example, minter is the output of mint transaction, it can be 1, multiple or even 0. If it is set to 1 each time when minting, the number of minters available in the entire network will remain the same (1), which will make mint crowded and everyone will need to grab this minter. In order to avoid this situation, it is necessary to set the number of minters output each time to be greater than 1, so that after minting, everyone will have more and more minters available.
However, each additional minter output means that you need to pay an additional utxo. For economic reasons, more people will be willing to set minter to 0, which will inevitably make minter deflationary. This requires some people to make contributions and voluntarily pay the extra minter.
In V2, two Minters are generated by default, and the status of the two Minters will be as close as possible.
Transaction Construction
Maybe some friends have found a problem, that is, why can we use Minters utxo to build transactions? To understand this problem, we need to analyze the source code of the contract.
1. Reveal UTXO
First, we analyze the transaction in the reveal process, and we find that it uses the output commit of the previous transaction as input. Why can we use a utxo that is not our address to construct the input of the transaction?
According to common sense, a private key corresponds to a public key, and the public key derives the address. When verifying whether an input utxo is valid, it is generally determined by comparing the signature after decryption with the public key to see if it is consistent with the original transaction. This part of the logic is written in the Bitcoin script. So we can cleverly rewrite the logic of the script. The public and private key pairs written in the script are our own addresses, so that we can control the utxo of two different addresses.
Looking at the source code we can see what happened:
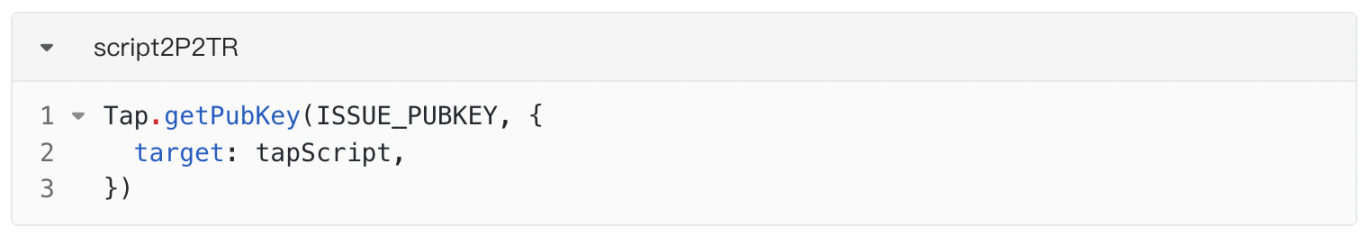
There is another problem here, that is, one private key corresponds to one public key, so why is the generated commit address different from our address? Here we can see from the source code
That is to say, our private key will adjust the public key according to an ISSUE_PUBKEY, which is also a feature of the P2TR address.
2. Minter UTXO
In the reveal process, we use different utxo as input, but the encryption key is the same, which is the deployers private key. However, in the minter stage, everyone can use these utxo as input. How is this possible?
I guess this part is the OP_CAT capability mentioned earlier, that is, the smart contract capability. Each minter is a smart contract. However, the source code of this part is not public yet, so I don鈥檛 know how it is implemented.
Transaction Status (V2)
In Minter, the state is also retained. This state exists in two places: one is in the OP_RETURN of the transaction output, and the other is stored in the smart contract, which is the Minter and Token mentioned above.
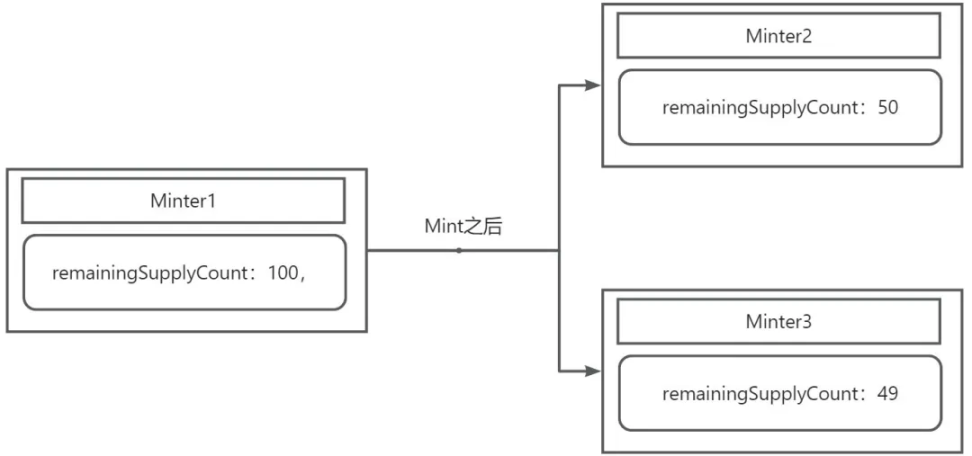
The Hash of the current transaction output status is stored in OP_RETURN, and the remaining number of mints of the token is stored in the contract. After each mint, the mint amount of the newly generated Minter will be equal to the remaining number of mints divided by two. Represented by a diagram:
When the game is finally over, the remaining number of all Minters is 0.
Back to the original picture, in addition to Minter being a smart contract, the generated token is also a smart contract, that is, CAT 20. CAT 20 has two basic states: quantity and the address of the token owner. You can see that unlike the previous BRC 20 or inscription, your CAT 20 is not on the UTXO of your address.
Transfer
When transferring, the number of input and output tokens in the transaction must be consistent. Of course, there can be multiple different tokens in the same transaction, as long as the input and output numbers of different tokens are consistent.
Burn
If you want to burn the token, just transfer the token to a normal address.
Resumir
As you can see, all operations are constructed by the users themselves, which is very flexible, so a lot of verification logic needs to be done in the contract part. Some of the vulnerabilities that have been exposed so far are also due to negligence in the verification logic.
This design can have some benefits:
-
If you want to find the holding status of all tokens, you only need to check the utxo of the token, and there is no need to continue to check upwards.
-
If you want to check the current status of mint, you can search for transactions with cat in the OP_RETURN data.
ZAN is here to get water without any threshold!
Tip: You can receive 0.01 ETH free testnet token every 24 hours to support your experience and testing of Web3 projects in the Ethereum ecosystem. Click to receive it now: https://zan.top/faucet?chInfo=ch_WZ
More public chains will be supported soon~
This article was written by Yeezo (X account @GaoYeezo 75065 ) del equipo ZAN (cuenta X @zan_team )
This article is sourced from the internet: CAT20: Token Protocol on Fractal BTC